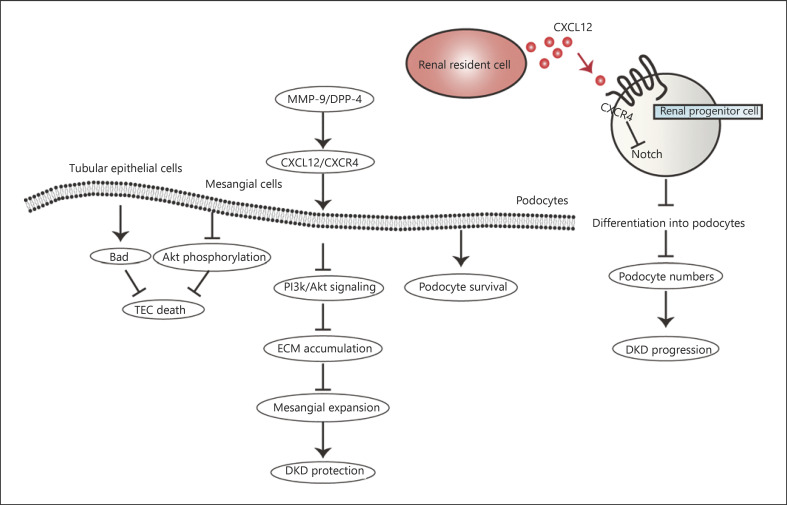
Fig. 2.
The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis-mediated signaling network in DKD. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis plays a dual regulatory role in DKD. On the one hand, CXCL12/CXCR4 leads to TEC decrease, mesangial expansion reduction, and podocyte survival, which contribute to diabetic renoprotection. TEC death is decreased via BAD and Akt phosphorylation while fibronectin expression and ECM accumulation are inhibited through PI3K/Akt signal pathway, reducing mesangial expansion. On the other hand, the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis mediates podocyte reduction by reducing podocyte progenitor cell differentiation into podocytes via inhibiting Notch signal transduction, resulting in DKD progression. DKD, diabetic kidney disease; TEC, tubular epithelia cell; ECM, extracellular matrix.