Figure 1.
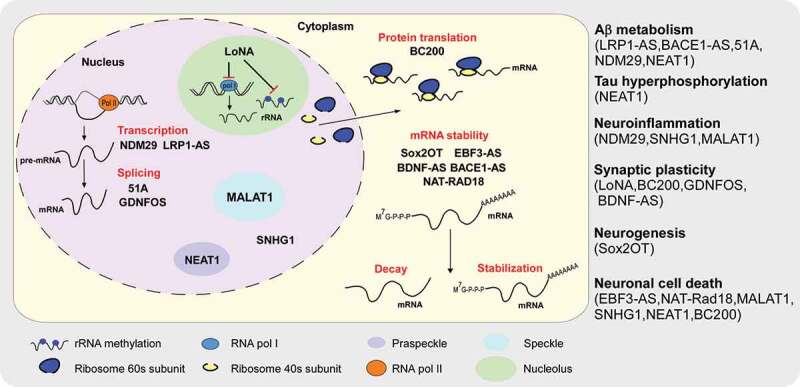
Schematic of LncRNAs and their regulatory mechanisms in AD. LncRNAs modulate cellular process such as mRNA transcription (NDM29 and LRP1-AS), mRNA splicing (51A and GDNFOS), mRNA stability (Sox2OT, EBF3-AS, BDNF-AS, BACE1-AS and NAT-RAD18), and protein translation (LoNA and BC200). LncRNAs participate in AD pathology via having impact on Aβ metabolism (LRP1-AS, BACE-AS, 51A, NDM29 and NEAT1), tau hyperphosphorylation (NEAT1), neuroinflammation (NDM29, SNHG1 and MALAT1), synaptic plasticity (LoNA, BC200, GDNFOS and BDNF-AS), neurogenesis (Sox2OT), and neuronal cell death (EBF3-AS, NAT-Rad18, MALAT1, SNHG1, NEAT1 and BC200)
