Figure 2.
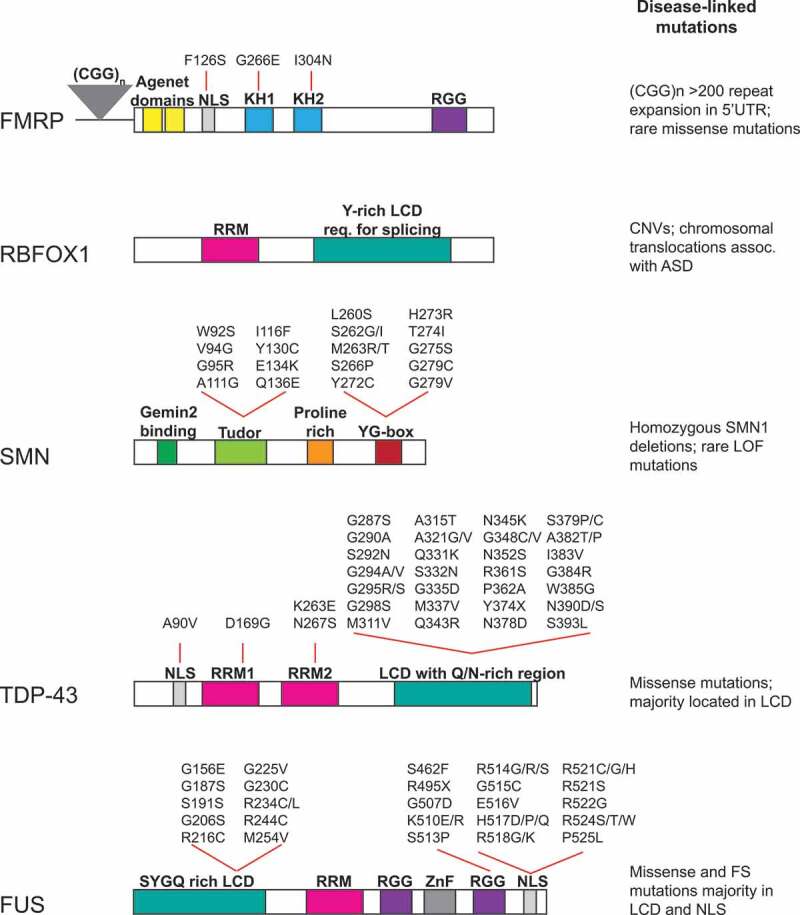
Schematic of RNA-binding protein domain structure, mutations, and disease mechanism. RBFOX1, FMRP, SMN, TDP-43 and FUS functional domains and locations of disease-linked mutations are highlighted. Abbreviations used: Nuclear localization signal (NLS); hnRNP K protein homology (KH); arginine-glycine-glycine box (RGG); RNA recognition motif (RRM); Low complexity domain (LCD); Zinc finger (ZnF); Tyrosine- and glycine-rich region (YG-box); Frameshift (FS); Loss of function (LOF)
