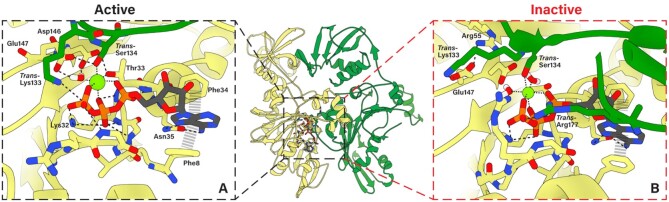
Figure 2.
ATP-binding poses predicted from MD simulations. (A) Active ATP-binding pocket contains canonically predicted interactions. The cis-acting (yellow) subunit's Walker A motif backbone NH groups bind the β-phosphate, Lys32 binds the γ- and β-phosphates, and Thr33 chelates Mg2+. Downstream of the Walker A motif, Phe34 and Asn35 function as the Q-motif, and bind the adenosine with help from N-terminal gate Phe8. The Walker B motif Asp146 and catalytic Glu147 isolate a single water molecule, which chelates Mg2+ (green sphere). Residues donated in trans from the neighboring subunit (green) also participate in ATP-binding. Notably, Lys133 is seen interacting with the γ-phosphate and Ser134 chelates Mg2+. (B) Inactive pose maintains many of the same interactions as the active pose, with a few key differences. Arg177 is now donated in trans to interact with the γ-phosphate, while Lys133 interacts with catalytic Glu147 away from the γ-phosphate. This interaction is stabilized by cis-acting Arg55.