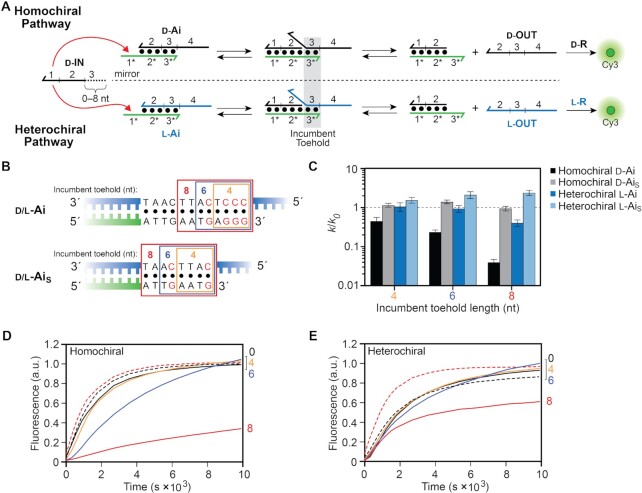
Figure 5.
The length and nucleotide composition of the incumbent toehold affects toehold exchange on PNA–DNA heteroduplexes. (A) Schematic illustration of the toehold exchange mechanism for both the homo- and heterochiral reaction pathways. (B) Sequences of the incumbent toehold domains within d/l-Ai and its truncated version d/l-AiS. Individual incumbent toeholds are boxed based on their length and red letters emphasize G/C base pairs. Incumbent toeholds are produced by truncating the input strand by the corresponding length. (C) Calculated rate constant as a function of incumbent toehold length (k) relative to the full-length input (k0) having no incumbent toehold. Error bars represent standard deviation from three independent experiments. (D, E) Fluorescence monitoring (Cy3) of toehold exchange for the homochiral (D) and heterochiral (E) reaction pathways. The length of the incumbent toehold is indicated on the right y-axis. Dotted lines indicate reactions carried out with the truncated PNA–DNA heteroduplex (AiS) for the indicated incumbent toehold lengths (black = 0-nt; red = 8-nt). Reactions depicted here were carried out as described in Figure 2.