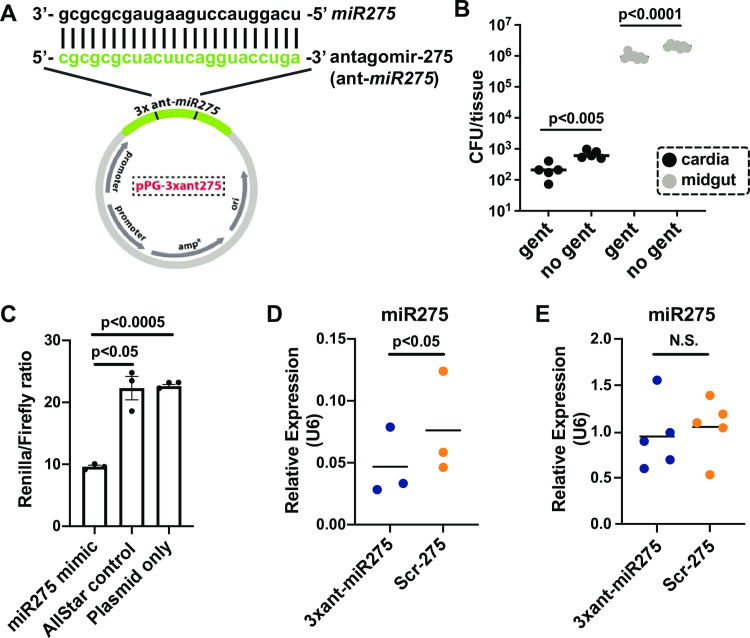
Fig 1. The successful development of paratransgenic expression system.
(A) recSodalis plasmid construct. Three tandem antagomir-275 repeats (3xant-miR275, in green) that are complementary to the tsetse miR275 mature sequence were cloned into plasmid pgRNA. Each repeat is separated by a 3-nucleotide linker sequence. 3xant-miR275, and a similarly engineered construct that encodes a scrambled antagomir-275 (Scr-275), were electroporated into SodalisWT to generate strains designated Sgm3xant-miR275 and SgmScr-275, respectively. (B) Quantification of Sgm3xant-miR275 within cells of tsetse’s cardia (black) and midgut (grey) via gentamicin exclusion assay. Each dot represents one tsetse organ (n = 5). A Student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. (C) Dual luciferase reporter assay. Each dot represents the average of normalized luciferase signal (Renilla/Firefly ratio) ± SEM of each experiment. The 3xant-miR275 construct was cloned into the psiCheck-2 plasmid containing two luciferase reporter genes, Renilla (reporter) and Firefly (internal control). The luciferase activity is measured by the Renilla signal normalized to the Firefly signal. Three different experiments were performed to test the binding efficacy between 3xant-miR275 and 1) synthetic miR275 mimic, 2) synthetic AllStars Negative Control, and 3) psiCheck plasmid without adding any miRNA. Three biological replicates (with 3 technical replicates each) per experiment were used. Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests were used to determine statistical significance. (D) miR275 expression level in the midgut of paratransgenic Gmm3xant-miR275 versus GmmScr-275 flies. Each dot represents 5 individual midguts. A student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. (E) miR275 expression in the cardia of Gmm3xant-miR275 versus GmmScr-275 flies. Each dot represents 5 individual cardia. A student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis.