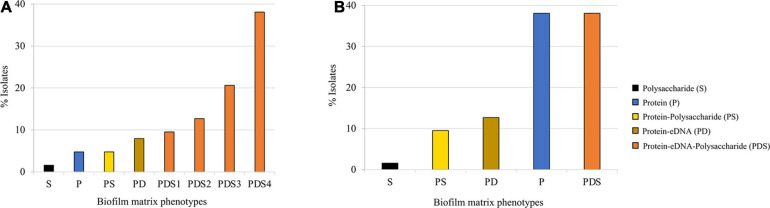
FIGURE 1.
Quantitative classification of preformed biofilm in 63 Staphylococcus saprophyticus strains based on matrix phenotypes. (A) Activity of biofilm-degrading agents, namely, proteinase K, DNase, and sodium periodate, was assessed on biofilm produced. Isolates with >70% biofilm reduction after treatment with specific biofilm detaching agents were interpreted to be composed of the component targeted by the disruptor, while 30–70% or <30% biofilm reduction after disruption were expressed as partially composed or not composed of the targeted biofilm components, respectively. S, polysaccharide; P, protein; PS, protein–polysaccharide; PD, protein–partial eDNA; PDS1, protein–polysaccharide–partial eDNA; PDS2, protein–partial polysaccharide–eDNA; PDS3, protein–eDNA–partial polysaccharide; and PDS4, protein–polysaccharide–eDNA. (B) Biofilm matrix phenotypes were categorized based on the major component such that components that were partially present (30–70% biofilm detached) in the biofilm produced by isolates were excluded. S, polysaccharide; PS, protein–polysaccharide; PD, protein–partial eDNA; P, protein; and PDS, protein–polysaccharide–eDNA. Assays were carried out in triplicates. All assays were carried out in triplicates.