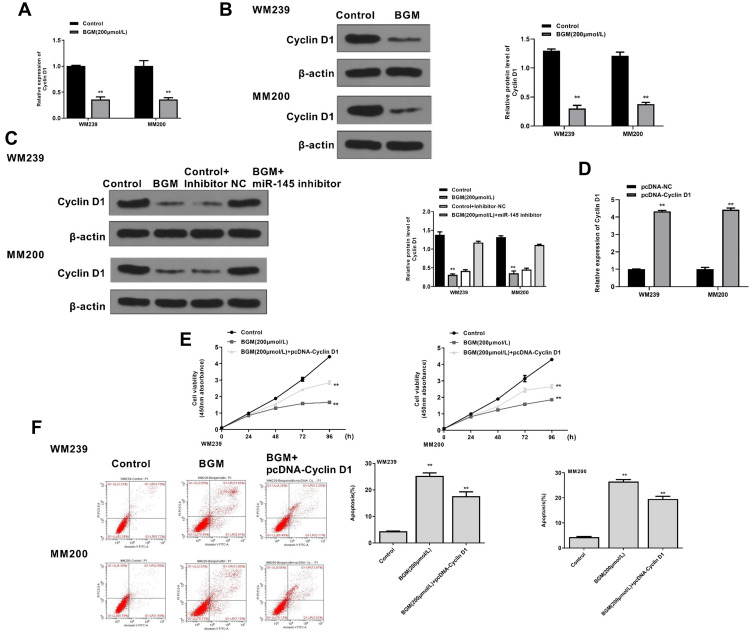
Figure 6.
BGM inhibits the progression of melanoma by targeting miR-145/Cyclin D1 axis in vitro. (A and B) The WM239 and MM200 cells were treated with BGM at indicated dose. (A) The mRNA expression of Cyclin D1 was assessed by qPCR assays in the cells. (B) The protein expression of Cyclin D1 and was tested by Western blot analysis in the cells. The results of Western blot analysis were quantified by ImageJ software. (C) The WM239 and MM200 cells were treated with BGM at the indicated dose, control inhibitor, or co-treated with BGM and miR-145 inhibitor. The protein expression of Cyclin D1 and β-actin was measured by Western blot analysis in the cells. (D) The WM239 and MM200 cells were transfected with pcDNA control vector or pcDNA-Cyclin D1 overexpression vector. The expression of Cyclin D1 was analyzed by qPCR assays in the cells. (E and F) The WM239 and MM200 cells were treated with BGM at the indicated dose or co-treated with BGM and pcDNA-Cyclin D1 overexpression vector. (E) The cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assays in the cells. (F) The cell apoptosis was measure by flow cytometry analysis in the cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistic significant differences were indicated: **P < 0.01.