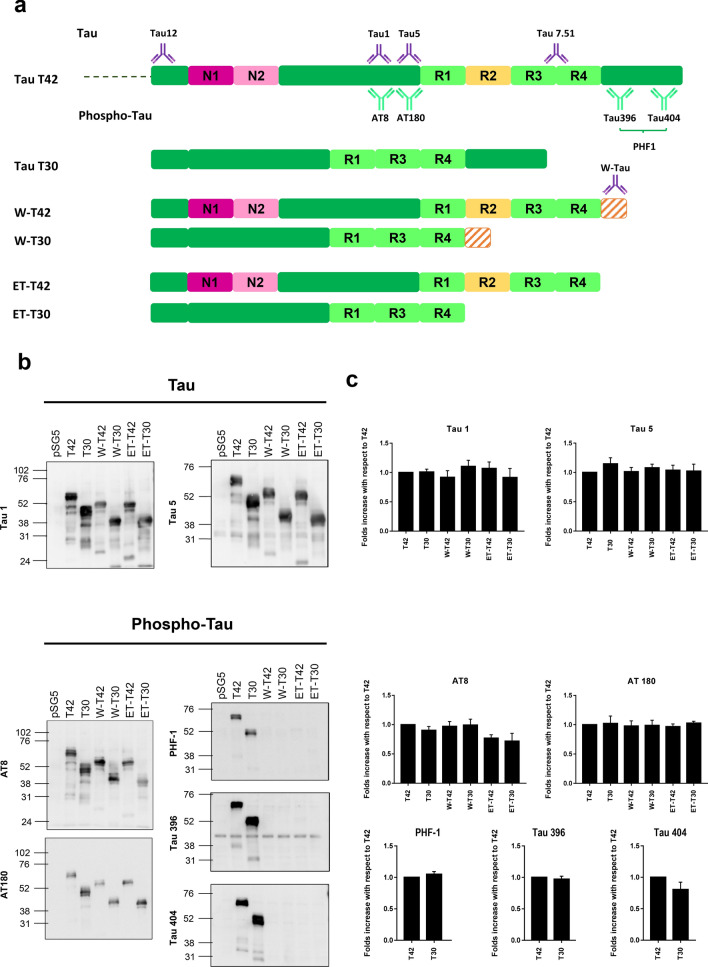
Fig. 3.
W-Tau phosphorylation pattern. a Schematic representation of different Tau protein isoforms: full-length isoform with four repeats (R) and two insertions (N) (T42), full-length isoform with three repeats and no insertions (T30), the truncated by intron retention isoforms W-Tau with four repeats, two insertions and an extra peptide (W-T42) or with three repeats, no insertions and the extra peptide (W-T30); and the correspondent asparagine-endopeptidase-truncated isoforms (ET-T42 and ET-T30). Representation of the antibodies recognizing the Tau molecule at their corresponding epitopes: Antibodies recognize all isoforms of Tau (Tau12 on amino acids 6–18; Tau 5 on amino acids 210–241 and Tau 7.51 on amino acids 315–376) or specific against dephosphorylated Tau in residues Ser195, 198, 199 and 202 (Tau1), and phospho-Tau in residues Ser202/Thr205 (AT8), Thr231 (AT180), Ser404 (Tau404), Ser396 (Tau396) and Ser396/Ser404 (PHF1). W-Tau antibody recognizes the unique peptide present on W-Tau isoforms. b Samples from HEK293T cells transfected with the different isoforms were probed with different antibodies for phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated Tau. c Quantification of the data of different Tau epitopes with respect to total Tau measured with Tau 7.51 antibody, showing mean and SEM (n = 4). One-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons followed by a Kruskal–Wallis test was performed to compare each isoform and T42 full-length level of phosphorylation