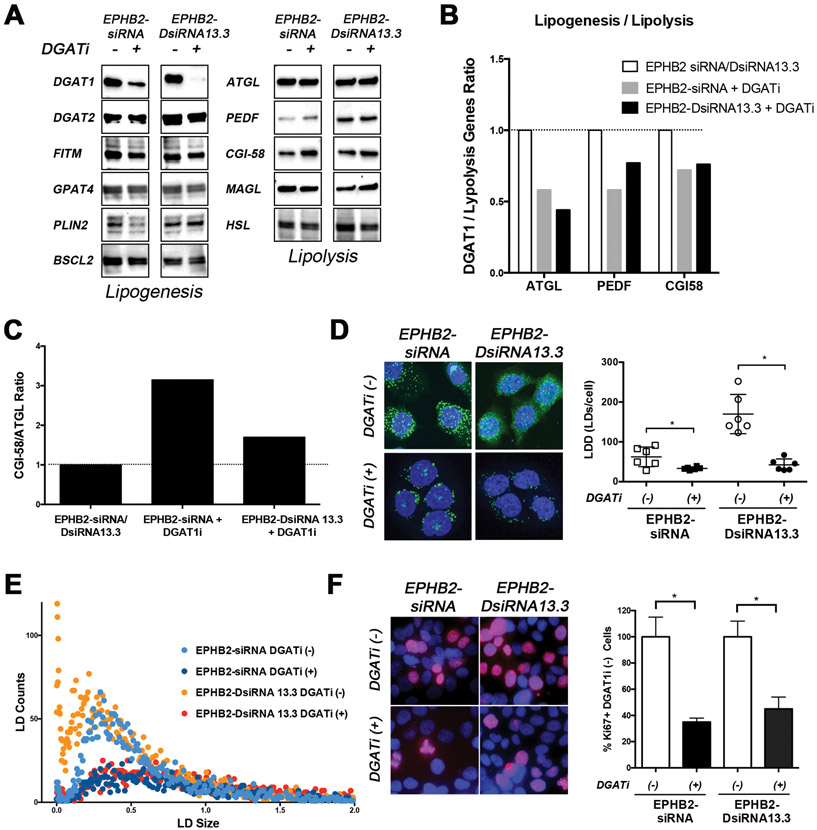
Figure 5. DGAT1 inhibition reverses EPHB2 loss lipid-induced changes.
A. EPHB2 engineered BPH1 cells were exposed to a DGATi for 48hr before protein isolation. Western blot images show a clear effect of DGAT1 inhibition on the protein levels. The expression of key lipogenesis and lipolysis-related genes were assessed. B. Quantitation of DGAT1/lipolysis genes including ATGL, PEDF and CGI58 in EPHB2 silenced cells exposed to the DGAT1 inhibitor compared to the absence of DGAT1 inhibition. C. The CGI-58/ATGL ratio based on protein expression was analyzed in EPHB2 knock down cells treated with DGAT1 inhibitor and compared to untreated cells. D. NileRed staining of EPHB2 knock-down BPH1 cells in the presence/absence of DGAT1 inhibitor (Left). Cells exposed to the DGAT1 inhibitor exhibited a significant decrease in LD density compared to untreated cells (Right). E. Dot plot analysis of LD distribution shows a clear reduction of newly formed (smaller size) LDs in EPHB2 knock down cells after treated with DGAT1 inhibitor (dark blue and red dots). F. Dual Ki67 (red) and DAPI (blue) immunofluorescence of BPH1 silenced cells with EPHB2 siRNA or DsiRNA13.3 in the presence/absence of a DGAT1 inhibitor (Left). Quantitation of Ki67 positive cells exposed to DGAT1 inhibitor was compared to control untreated cells (Right). * = p<0.05