Figure 1. System for Homeostatic Oxygen Sensing.
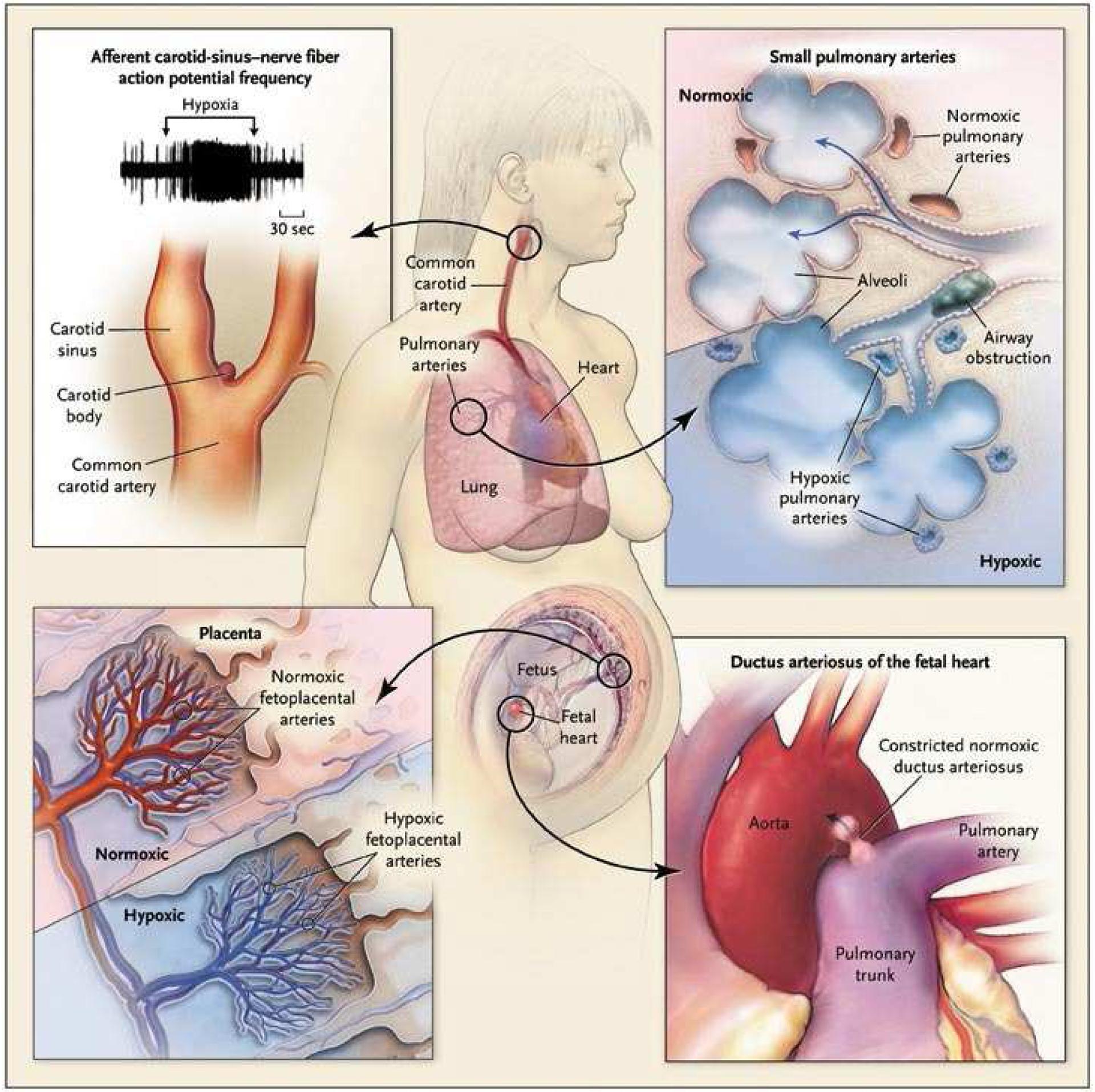
The homeostatic oxygen-sensing system (HOSS) is made up of specialized tissues specifically adapted to sense small changes in oxygen levels. These include the type 1 cells within the carotid body, smooth muscle cells (SMC) within the resistance pulmonary arteries (PA), fetoplacental arteries, and ductus arteriosus. Hypoxia increases the afferent carotid-sinus nerve fiber action potential frequency, which stimulates respiration. Hypoxia also elicits vasodilation of the ductus arteriosus and systemic arteries, while stimulates vasoconstriction of the fetoplacental and resistance PA.
Copyright © New England Journal of Medicine
