Figure 2. The mechanism of acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.
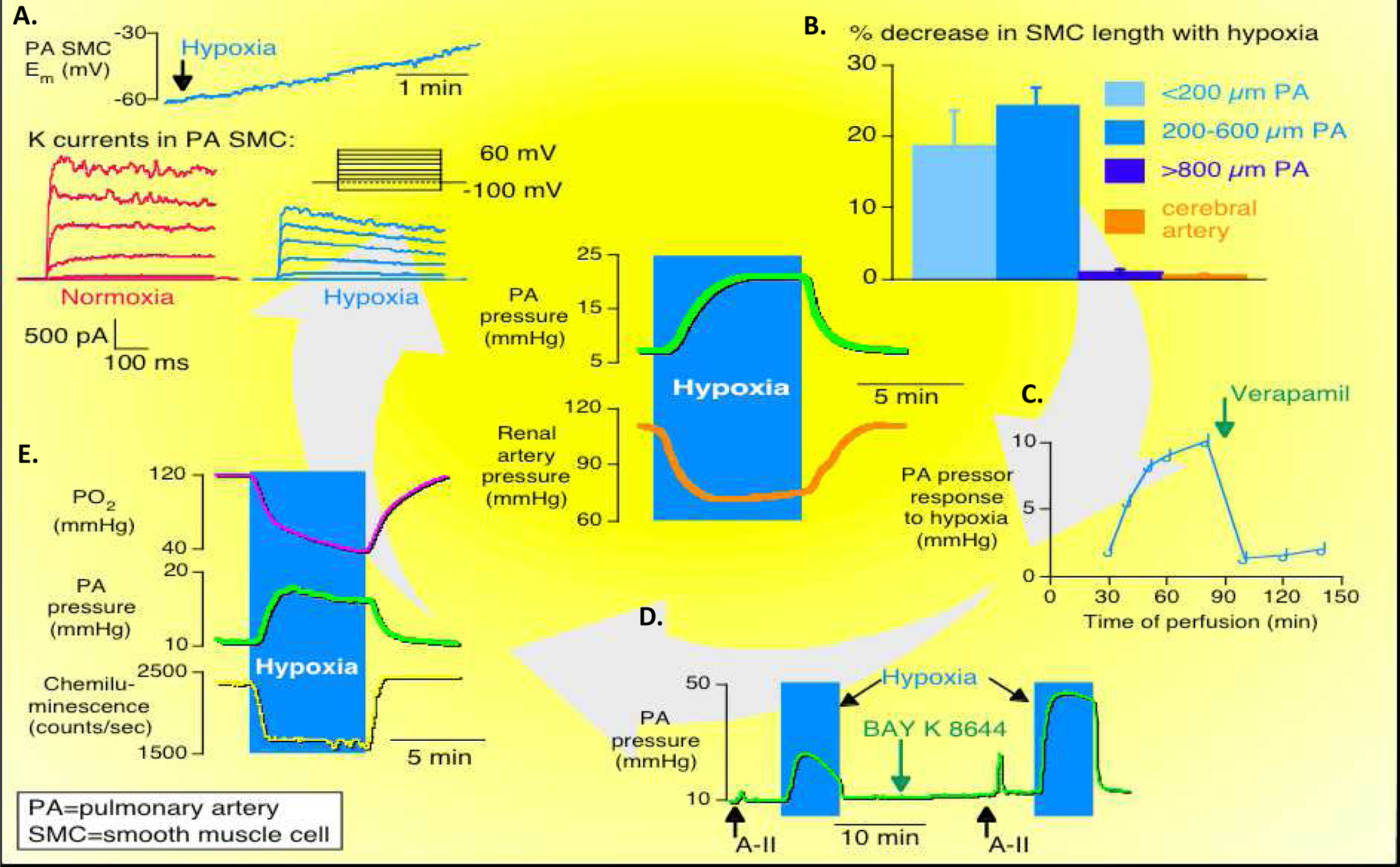
Middle: Pulmonary artery (PA) pressure is increased during hypoxia while renal artery pressure is decreased during hypoxia.
A. Potassium channel current is reduced in PA smooth muscle cells (SMC) during hypoxia.
B. Percentage decrease in SMC length with hypoxia is only observed in PAs with diameters of less than 600μm.
C. PA pressure response to hypoxia is abolished by treatment with verapamil, a calcium channel blocker.
D. PA pressure response to hypoxia is increased by BAY K8644, a calcium channel agonist.
E. PA pressure increases in response to decreased pO2.
Copyright © The FASEB Journal
