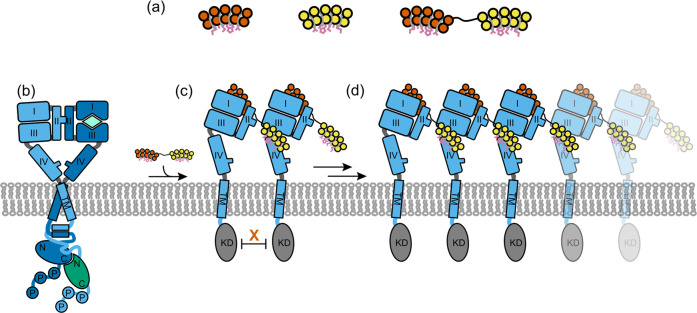
Fig. 1. Concept of bipDARPins and possible modes of binding to HER2.
a Monovalent, monoparatopic DARPins (9.26 binding to extracellular subdomain I, vermillion; G3 binding to extracellular subdomain IV, yellow) and design of bipDARPin 6L1G (right), connecting 9.26 and G3 through a short linker. b Ligand-activated (e.g., by heregulin, mint) HER2:HER3 (sky blue, blue) heterodimers are able to stimulate proliferation and survival. c, d Bivalent intermolecular binding of bipDARPins may induce the formation of (c) inactive dimers or (d) oligomerization into daisy chains. In both cases, the kinase domains are separated and thus inactive. HRG heregulin, TM transmembrane helix, KD kinase domain.