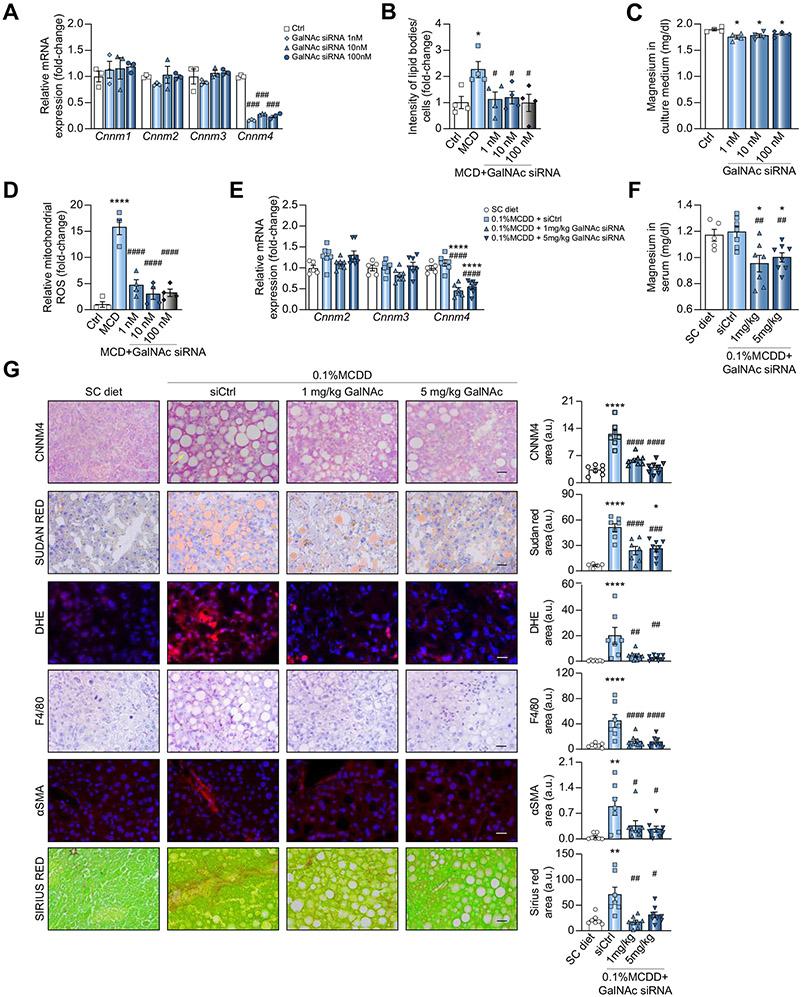
Fig. 7. Inhibition of CNNM4 expression by GalNAc)–siRNA conjugate reduces NASH in preclinical models.
Levels of (A) Cnnm1-3 mRNA and (C) magnesium in extracellular medium from primary hepatocytes treated overnight with a GalNAc-conjugated siRNA against Cnnm4 (GalNAc siRNA) and a MCD medium. Relative determination of (B) lipid accumulation and (D) mitochondrial ROS production in primary hepatocytes treated with an MCD and Ctrl or GalNAc siRNA. Relative levels of (E) Cnnm1-4 mRNA and (F) Mg2+ in serum, and (G) histological characterisation of CNNM4, lipids (Sudan Red), inflammation (F4/80 and DHE) and fibrosis (αSMA and Sirius Red) in livers from mice fed a 0.1% MCDD and treated with siCtrl or GalNAc siRNA. *p <0.05, **p <0.01, and ****p <0.0001 vs. Ctrl/SC diet; #p <0.05, ##p <0.01, ###p <0.001, and ####p <0.01 vs. MCD + siCtrl/0.1% MCDD + siCtrl. CD-HFD, choline-deficient high-fat diet; CNNM4, cyclin M4; DHE, dihydroxyethyl; GalNAc, N-acetylgalactosamine; MCD, methionine and choline deficient; MCDD, MCD diet; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; ROS, reactive oxygen species; siRNA, small interfering RNA.