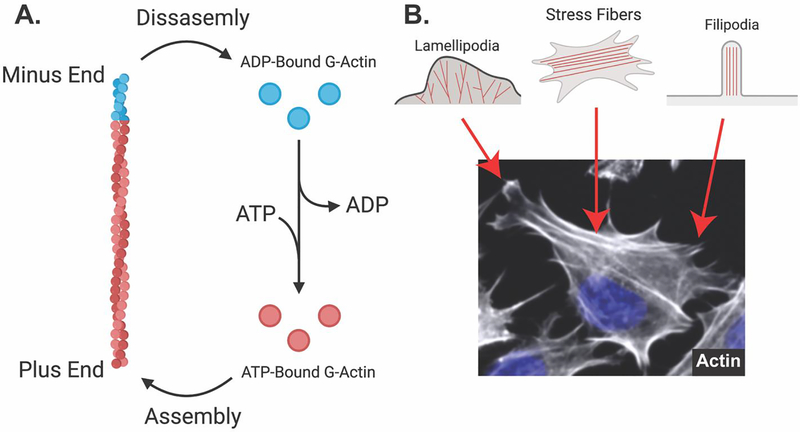
Figure 4: Actin microfilaments are dynamic and assemble into different structures in osteocytes.
A. Globular actin monomers bound to ATP are assembled into actin microfilaments (F-actin) on the plus end. Intrinsic ATP-ase activity of actin microfilaments facilitates the cleavage of ATP to ADP, which favors disassembly on the minus end. ADP-bound G-actin exchanges ADP for ATP, again promoting polymerization. B. Fluorescent staining (phalloidin) of Ocy454 cells shows different actin-based structures. Lamellipodia contain branched actin filaments and show ruffled membrane edges. Stress fibers contain bundles of actin filaments that feed into filipodia. Filipodia facilitate the formation of focal adhesions, attaching the cellular cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix.