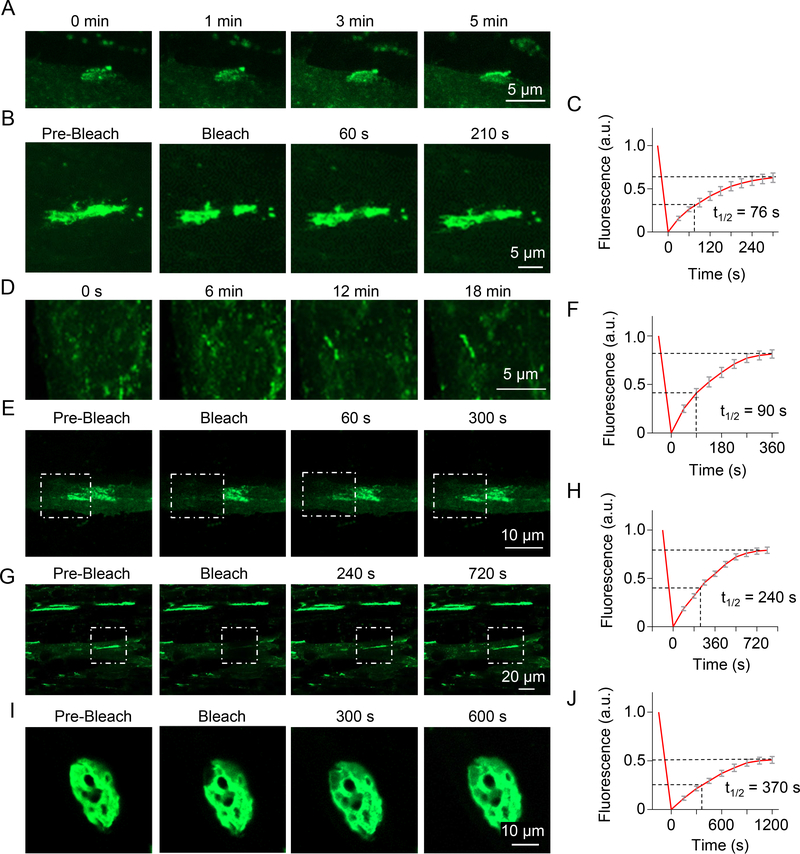
Figure 3. Rapsn LLPS into liquid-like compartments in myotubes and in muscles.
(A) Fusion of small spontaneous Rapsn-EGFP aggregates into large, continuous clusters in myotubes. Arrow, cluster during fusion.
(B) Dynamic property of Rapsn-EGFP protein within spontaneous clusters.
(C) Quantification of fluorescence recovery in (B).
(D) Fusion of agrin-induced Rapsn-EGFP clusters in myotubes.
(E-H) Dynamic exchange of Rapsn-EGFP between cluster and surrounding milieu, and within cluster in myotubes. (E) FRAP analysis of a agrin-induced Rapsn-EGFP cluster, and (F) quantification of fluorescence recovery; (G) FRAP analysis of a part of cluster and (H) quantification of fluorescence recovery.
(I, J) Dynamic property of Rapsn-EGFP in living muscles.
Data was shown as mean ± SEM; n = or > 3.