FIGURE 2.
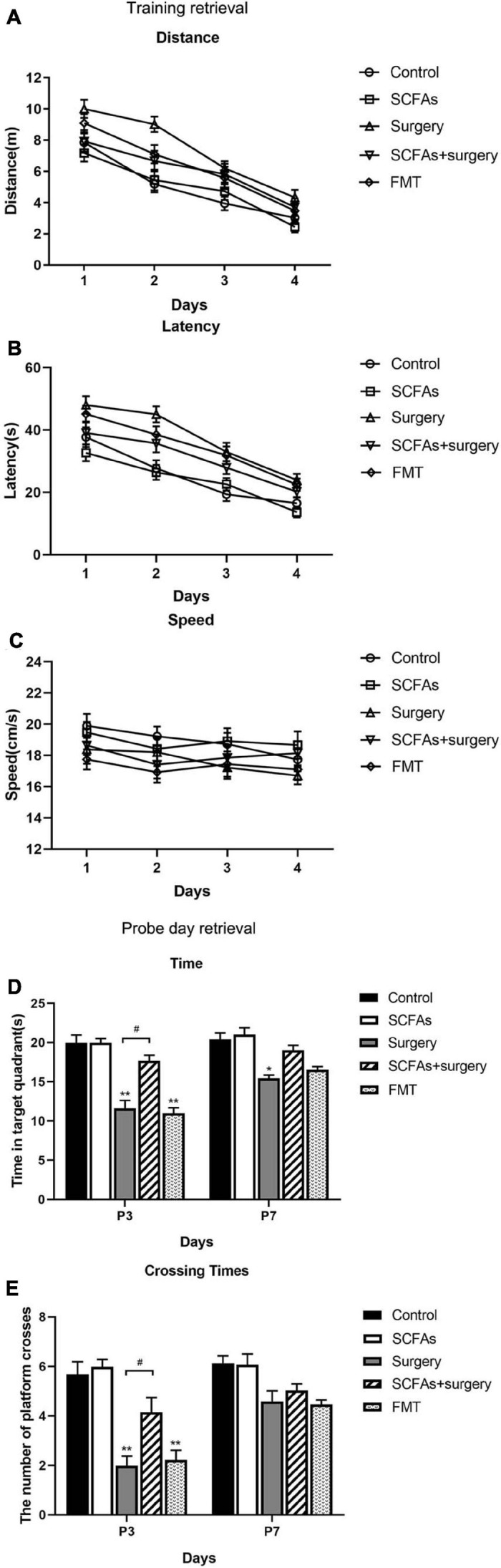
All mice showed improvements in swimming latency and distance over 4 consecutive training days in a Morris water maze (MWM). The mice in the SCFAs + surgery group performed better (swam less distance and less latency) than those in the surgery group on training days 2 and 3. Surgical trauma and anesthesia and fecal microbiota transplantation significantly exacerbated spatial learning and memory impairment in the probe trial test compared with the controls on postoperative or post-transplantation day 3. (A) Distance traveled to the platform. (B) Escape latency to the platform. (C) Swimming speed. (D) Time spent in target quadrant. (E) Cross platform times. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs. the day-matched control group, **p < 0.001 vs. the day-matched control group, #p < 0.05 vs. the day-matched surgery group. P3 and P7: postoperative or post-transplantation days 3 and 7, respectively.
