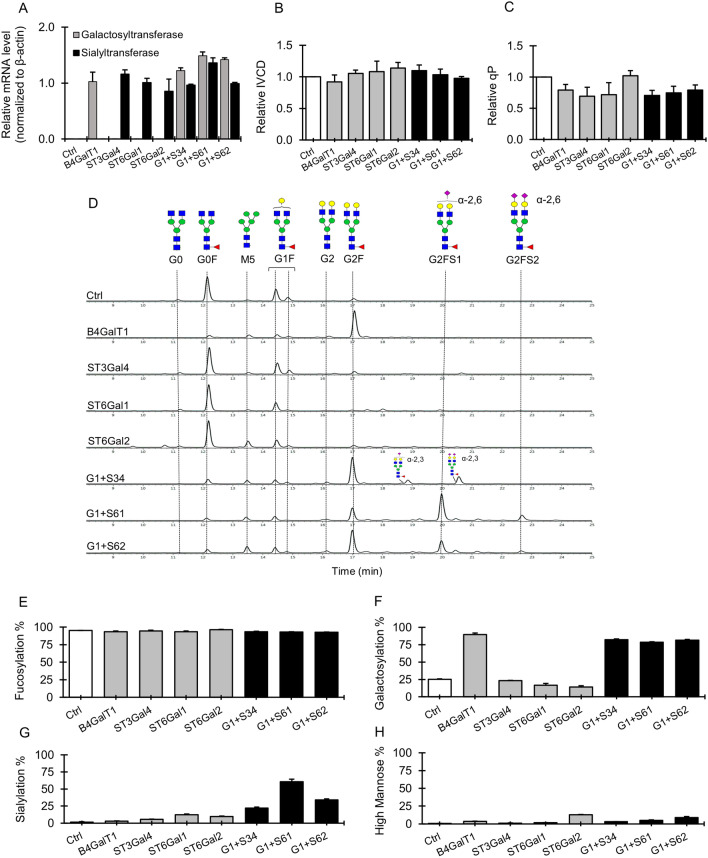
Figure 3.
Impact of co-expressing B4GalT1 and sialyltransferase isoenyzmes on the growth, productivity and glycosylation of antibodies in stably transfected CHO cell pools. All stable pools were generated through RMCE. The control pools expressed IgG rituximab LC, HC and DsRed genes. Other stable pools expressed IgG rituximab LC and HC genes, B4GalT1 and ST6Gal1 either individually or in combination, and DsRed. G1 + S34, G1 + S61, G1 + S62 are combinatorial stable pools co-expressing B4GalT1 and either of ST3Gal4, ST6Gal1 and ST6Gal2 gene, respectively. All stable pools were characterized in 7-day fed-batch cultures. (A) Relative galactosyltransferase/ sialyltransferase transcript levels in different stable pools to the internal control, β-actin (ACT) as determined by quantitative real time-PCR (qRT-PCR). (B–C) Relative change in the integrated viable cell density (IVCD) and specific productivity (qP) of each stably transfected pool to the control. (D) Aligned HILIC chromatograms of N-linked glycans on antibodies in different stable pools. Chromatograms shown are one of biological replicates with similar results. (E–H) Relative distribution of fucosylation, galactosylation, sialylation and high-mannose on antibodies produced different stable pools. Each point represents the average and standard deviation of measurements from two independent stably transfected pools.