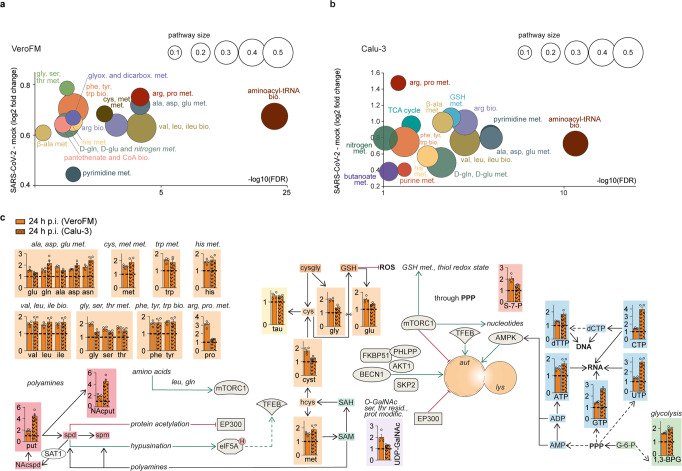
Fig. 1. SARS-CoV-2 causes accumulation of key metabolites in infected cells.
a, b Analysis and regulation of significantly altered pathways of mock- and SARS-CoV-2-infected (24 h p.i., MOI = 0.1) VeroFM cells (a) or Calu-3 cells (b). The y-axis shows the (median) log2 fold change (FC) of all significantly altered metabolites of the indicated pathway while the –log10 corrected p-value (false discovery rate (FDR)) is shown on the x-axis. The size of the circles illustrates the number of significantly changed metabolites in relation to all metabolites of a specific pathway. c Analysis of the autophagic pathway and the involved metabolites: ‘amino acids’ and ‘GSH metabolism’ (orange), ‘nucleotides’ (blue), ‘glycolysis’ (green), ‘polyamine metabolism’ (red) and ‘O-GalNAcylation’ (purple) in mock- and SARS-CoV-2-infected (24 h p.i.) VeroFM and Calu-3 cells. For a–c Error bars represent SEM. n = 4 biological samples per group of one experiment. All p-values were determined by a two-way ANOVA and Tukey´s post hoc test. FDRs were adjusted using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Abbreviations: 1,3-BPG, 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid; 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglyceric acid; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AKT1, RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; ala, alanine; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; arg, arginine; asn, asparagine; asp, asparagine; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; aut, autophagosome; BECN1, beclin-1; bio., biosynthesis; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; CoA, coenzyme A; cys, cysteine; cysgly, cysteinylglycine; cyst, cystathionine; dCTP, deoxycytidine triphosphate; dicarbox., dicarboxylate; elF5AH, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A hypusinated; EP300, histone acetyltransferase p300; F1P, fructose 1-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; F-1,6-BP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; FKBP51, 51 kDa FK506-binding protein; G6-P, glucose 6-phosphate; gln, glutamine; glu, glutamic acid; gly, glycine; glyox, glyoxylate; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GTP, guanosine triphosphate; hcys, homocysteine; his, histidine; ile, isoleucine; lac, lactic acid; leu, leucine; lys, lysine; mal, malic acid; met, methionine; met., metabolism; modific., modification; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NAcput, N-acetylputrescine; NAcspd, N-acetylspermidine; orn, ornithine; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvic acid; phe, phenylalanine; PHLPP, PH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; pro, proline; prot., protein; put, putrescine; pyr, pyruvic acid; resid., residue; ROS, reactive oxygen species; S7P, sedoheptulose-7-phosphate; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAT1, diamine acetyltransferase 1; SKP2, S-phase kinase-associated protein 2; ser, serine; spd, spermidine; spm, spermine; tau, taurine; TFEB, transcription factor EB; thr, threonine; trp, tryptophan; tyr, tyrosine; UDP-GalNAc, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine; UDP, uridine diphosphate; UTP, uridine triphosphate; val, valine.