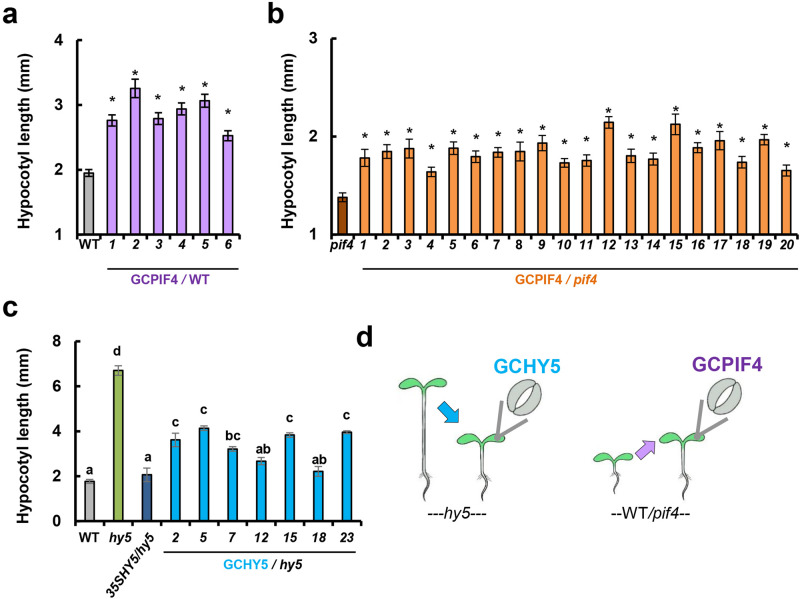
Fig. 5. Expression of PIF4 (GCPIF4) and HY5 (GCHY5) in guard cells affects hypocotyl elongation.
a GCPIF4 in the WT background (purple columns) stimulates hypocotyl elongation of independent GCPIF4/WT lines relative to the WT. b GCPIF4 in the pif4-mutant background (orange columns) stimulates hypocotyl elongation of independent GCPIF4/pif4 lines. c Hypocotyl lengths of independent lines expressing HY5 in the guard cells (GCHY5/hy5) or globally under the 35S promoter (35SHY5/hy5) in the hy5-mutant background (light-blue columns). Data points for (a–c) are means ± SE (n = 20–25 for a; n = 15–25 for b; n = 13–25 for c). a, b Asterisks indicate significant differences relative to the WT (Dunnett’s test, P < 0.05). c Different letters indicate a significant differences (Tukey’s HSD test, P < 0.05). d The illustration indicates the gene expressed in guard cells (GCHY5 or GCPIF4) and the genomic background (hy5, WT/pif4). The blue and purple arrows indicate the hypocotyl-growth response stimulated by GCHY5 and GCPIF4, respectively.