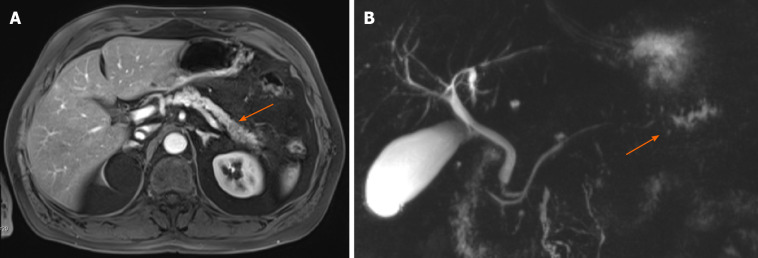
Figure 3.
Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. A: Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. A hypo-intense lesion (A, arrow) is causing a pancreatic duct stenosis with upstream dilatation of the pancreatic duct (B, arrow).