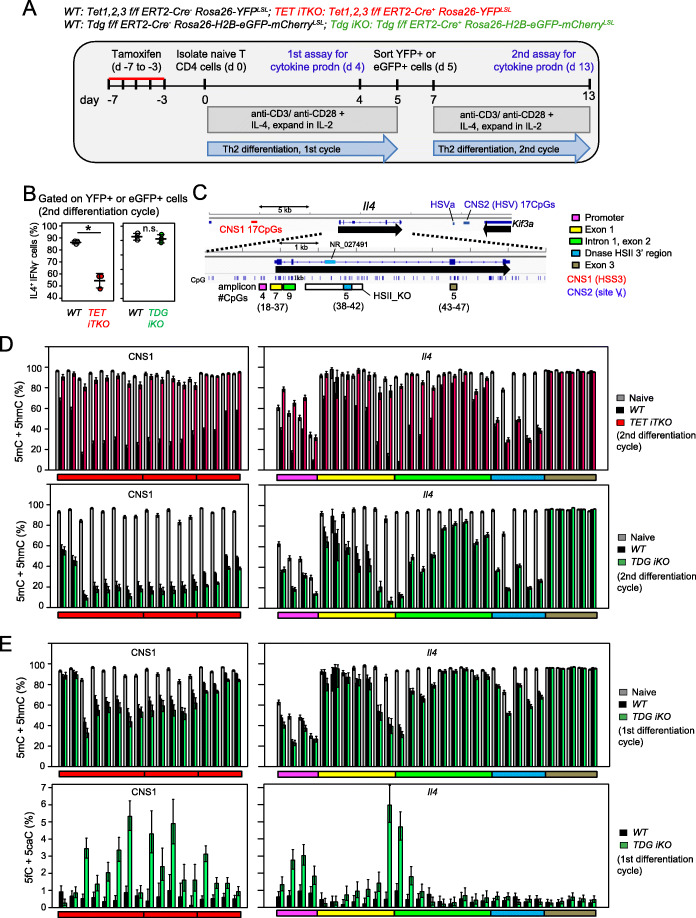
Fig. 1.
TET enzymes are important, but TDG is dispensable, for IL-4 production and DNA demethylation of the Il4 locus. A Flowchart of experiments. B Quantification of IL-4 production by Th2 cells after the second cycle of differentiation of naïve T cells from WT vs. TET iTKO, or WT vs. TDG iKO mice. C Schematic representation of the Il4 locus. The locations of all CpGs, the locations of PCR amplicons, and the numbers of CpGs per amplicon are indicated. D Bar graphs show the percentage of (5mC + 5hmC)/total C in 47 CpGs in the Il4 locus with confidence intervals (CIs) in WT vs. TET iTKO cells (upper), or WT vs. TDG iKO cells (lower), as determined by BS-seq. Results for naïve CD4+ T cells and Th2 cells after the second cycle of differentiation are shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Note that the CNS1 enhancer and the intronic enhancer near the border of exon 1 and intron 1 undergo substantial demethylation during Th2 differentiation. E Bar graphs show the percentages of (5mC + 5hmC)/total C (upper) and (5fC + 5caC)/total C (lower) in 47 CpGs in the Il4 locus in WT vs. TDG iKO cells, as determined by BS-seq (upper) and PB-seq (lower). Results for naïve CD4+ T cells (adapted from D) and Th2 cells after a single cycle of differentiation are shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments. TDG deficiency results in clear increases in 5fC/5caC, but no decrease in 5mC+5hmC, at CpGs that undergo TET-dependent demethylation. Statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05