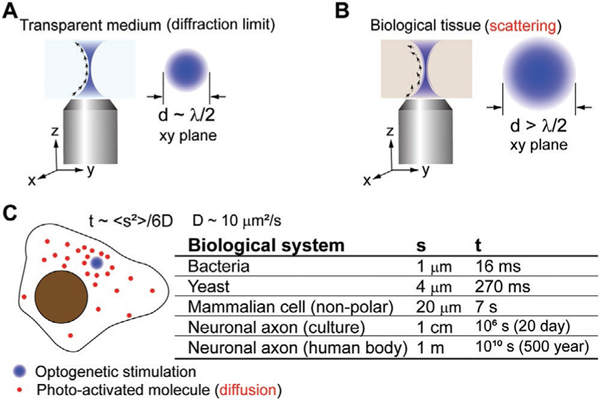
Figure 1.
A) Light diffraction limits the size of a coherent beam to approximately half of the excitation wavelength in lens-based optical microscopy. B) In opaque biological tissues, light scattering varies the coherent beam’s wavevector randomly and causes an expansion of the effective focal volume. C) molecular diffusion in cells further compromises the spatial resolution of the optogenetic stimulation. A back-of-envelop estimation of the traversing time of a small protein across a cell is presented. The typical value of a small protein’s diffusion coefficient in the cytoplasm is selected based on experimental measurement.[3]