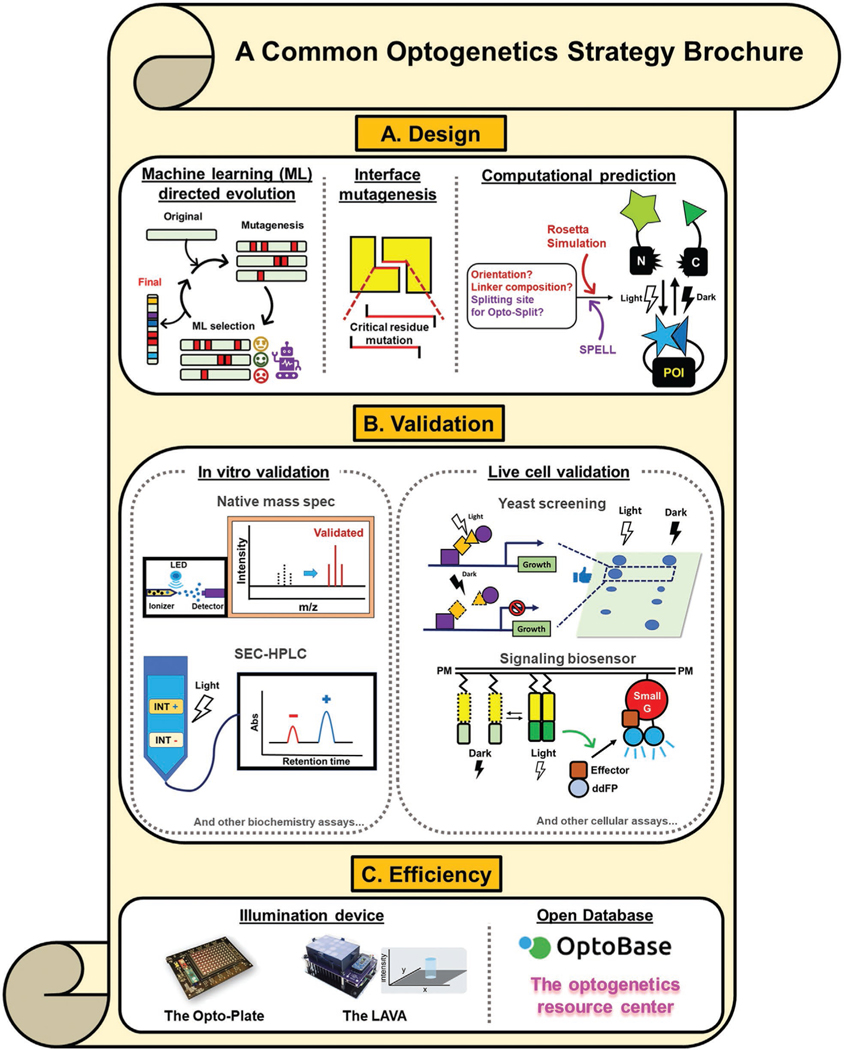
Figure 4.
Collection of commonly used optogenetic strategies. a) Optically active protein design and engineering approaches. POI: Protein of interest. b) Live cell or in vitro validation modules. INT+: Positive interaction; INT−, negative interaction; ddFP, dimerization-dependent fluorescence protein c) Efficient resources for conducting an experiment or collecting data. References of each strategy are listed as follows: machine learning directed evolution,[119,120] interface directed mutagenesis,[122] computational prediction,[31,123,124] native mass spectrometry,[128] SEC-HPLC,[129] yeast screening,[122,130] signaling biosensor,[131] optoplate,[132] LAVA plate,[133] optobase,[1a] and the optogenetic resource center.[1] The image of the optoplate is reproduced with permission.[51b] Copyright 2018, The American Association for the Advancement of Science. The image of the LAVA plate is reproduced with permission.[133] Copyright 2020, Elsevier.