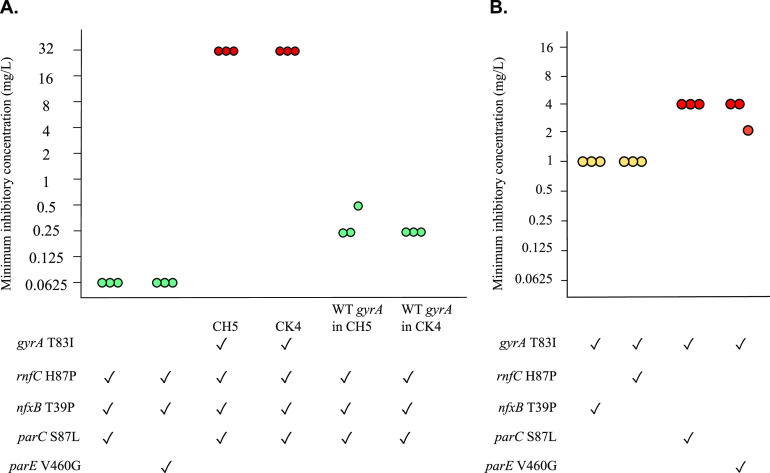
FIG 2.
A gyrA mutation is required for ciprofloxacin resistance. (A) Effects of combinations of mutations with and without a gyrA mutation. Mutants of strain PAO1 were engineered to contain combinations of rnfC, nfxB, parC, and parE mutations in the absence of a gyrA mutation, and also by replacing a gyrA mutation with the wild-type allele in experimentally evolved mutants CH5 and CK4. Genotypes of mutants are shown, where ✓ denotes the presence of mutation. (B) Effects of mutations in combination with a gyrA mutation. Mutants were engineered to contain the mutations shown. Each point represents one replicate of MIC testing. Turquoise, yellow and red denote susceptible (≤0.5 mg/liter), intermediate (1 mg/liter), and resistant range (≥2 mg/liter) of MICs, respectively.