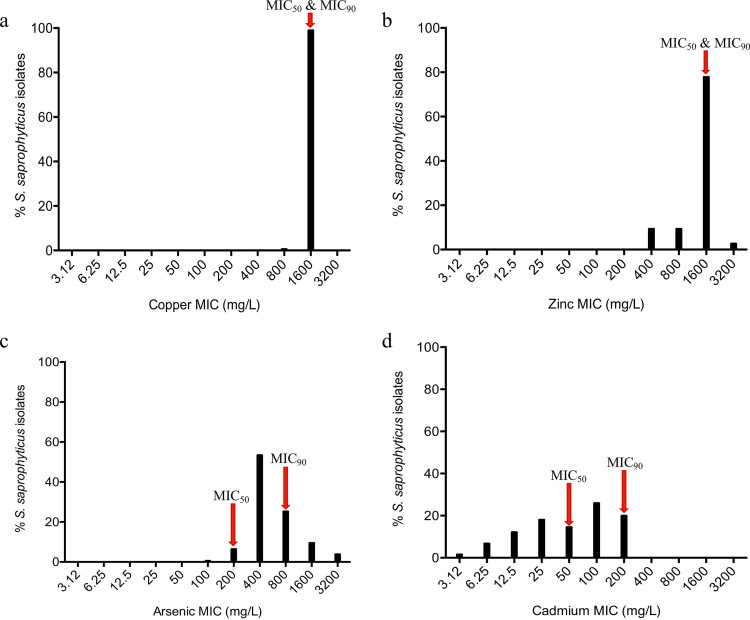
FIG 1.
MIC distribution of 422 Staphylococcus saprophyticus isolates recovered from human infection and colonization/contamination and environmental sources using the agar dilution method. Mueller-Hilton agar was supplemented with different concentrations (3.12 to 3,200 mg/liter) of copper (copper sulfate; CuSO4), zinc (zinc sulfate; ZnSO4), arsenic (sodium arsenite; AsNaO2), and cadmium (cadmium chloride; CdCl2). S. saprophyticus showed high resistance to copper (a) and zinc (b) (1,600 mg/liter). For arsenic (c), unimodal distribution was observed, which suggested epidemiological cutoff value (ECV) of ≥1,600 mg/liter. (d) A bimodal distribution was apparent for cadmium with a suggested ECV of ≥200 mg/liter.