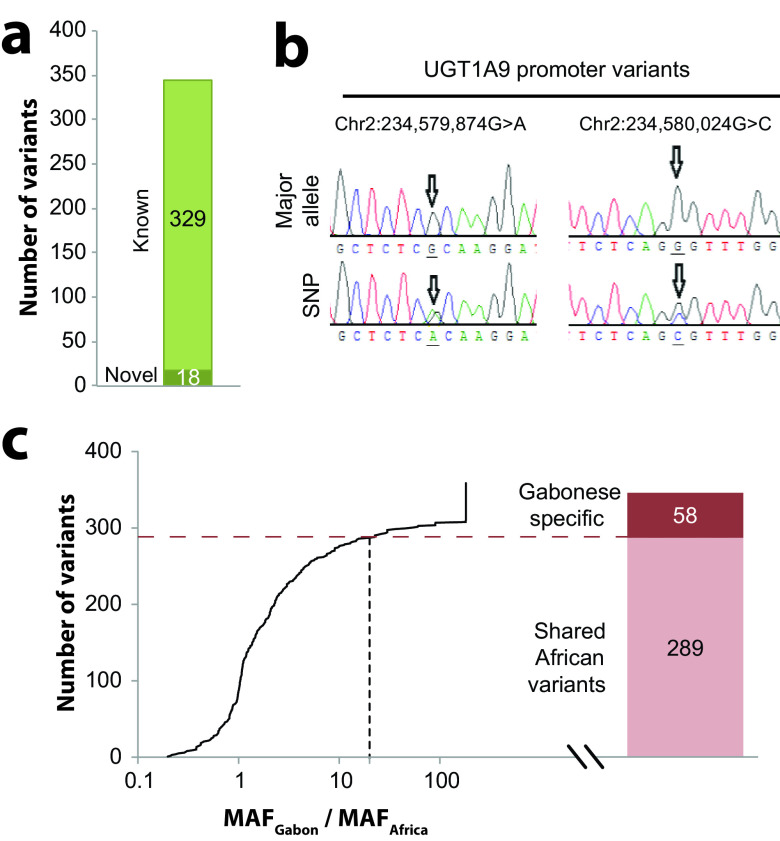
FIG 2.
The pharmacogenetic variability in Gabon is highly population specific. (a) Across all genes, 18 novel variations were identified, accounting for 4.6% of all variants. (b) Sanger sequencing data showing the nucleotide sequences (sense strands) in the promoter of UGT1A9. Major alleles are shown in the top row, while the bottom rows show the heterozygous variants. Arrows indicate the variant positions. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism. (c) Of all 347 detected variants, 16.7% (n = 58) were specific to the Gabonese population, as defined by a ≥20-fold increased minor allele frequency in Gabon (MAFGabon) compared to African reference populations (MAFAfrica), and each individual carried on average 2.2 population-specific pharmacogenetic variants.