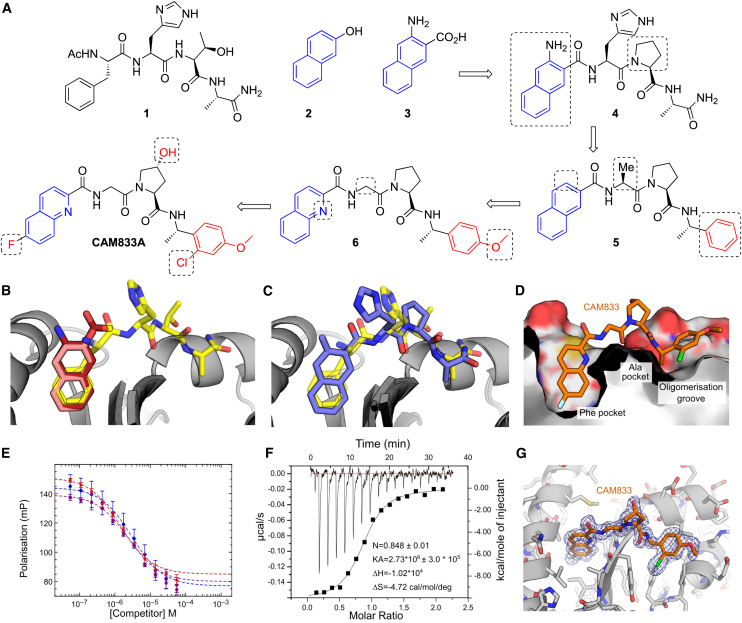
Figure 2.
Development of CAM833
(A) Merging of 3-amino-2-naphthoic acid (3) with FHPA tetrapeptide to yield 4. Trimming of the naphthyl and histidine group and replacement of terminal amide with phenyl group yields 5. Increase of polarity by replacing naphthyl with quinoline and adding methoxy group the phenyl ring results in 6. Further optimization leads to CAM833.
(B) Overlaid crystal structures of HumRadA1 in complex with 2-naphthol (2, PDB: 4B32, pink), 3-amino-2-naphthoic acid (3, PDB: 6TV3, dark red) and FHTA tetrapeptide (1, PDB: 4B3B, yellow).
(C) Structure of 4 (PDB: 6TWR, deep purple) in complex with HumRadA1 overlaid with FHTA peptide (PDB: 4B3B, yellow).
(D) Structure of CAM833 (orange, PDB: 6TW9) in complex with HumRadA22F. Side view of CAM833 complex with HumRadA22F showing partially cut surface of the protein and interaction of the fluoroquinoline ring with the Phe-pocket and the chloro-phenyl group binding into the oligomerization groove.
(E) Competition of BRC4 peptide binding to ChimRAD51 using FP assay with CAM833. Three independent measurements (triplicate technical repeats) of the same binding are shown in three different colors.
(F) Isothermal titration calorimetric measurement of direct binding of CAM833 to ChimRAD51. The baseline corrected thermogram is shown above with x and y axes above and left of the graph. The solid squares depict integrated heats for each titration point and solid line the fit to single-site binding mode with corresponding x and y axes below and to left of the graph.
(G) Refined 2FoFc electron density is shown for the ligand, contoured at 1σ.