Fig 2. LncRNA-PM knockdown in mouse cerebellum results in decreased Cbln1, impaired synapse integrity, and motor behavior.
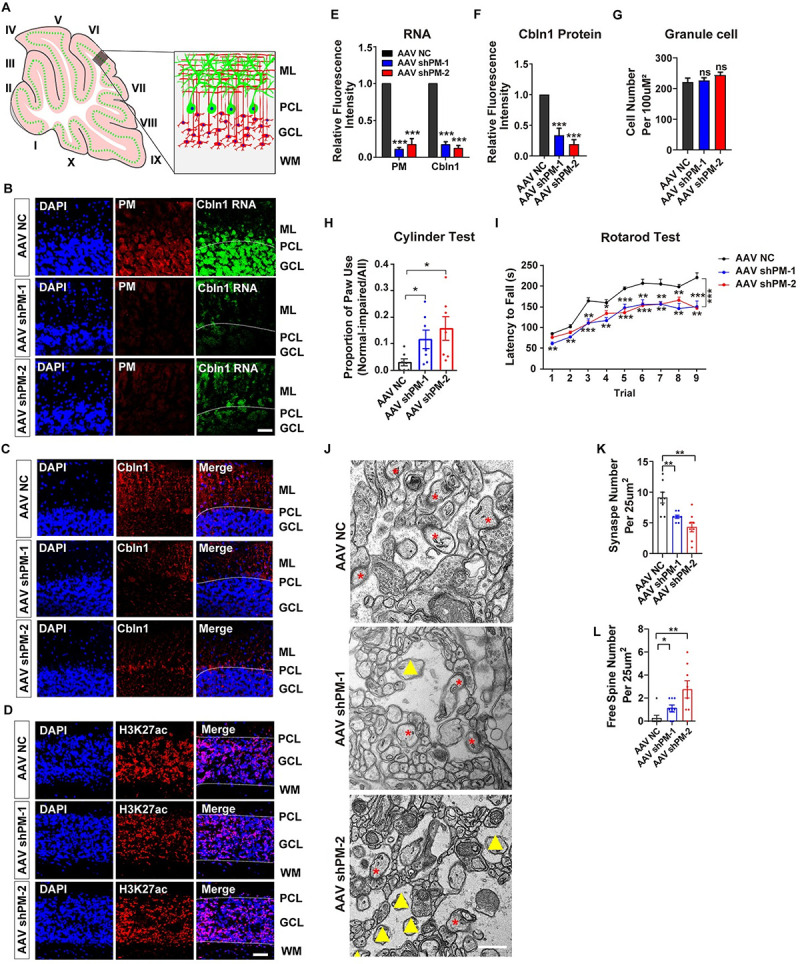
(A) Illustrated structure in the investigated cerebellar area. (B) The expression levels of PM (red) and Cbln1 (green) RNA in the cerebellar sections obtained from control (AAV NC) or lncRNA-PM (PM, red) shRNA-injected mice (AAV shPM-1 and AAV shPM-2). Scale bar, 40 um. (C and D) Immunofluorescence images of Cbln1 protein (C) and H3K27ac (D) in the cerebellar sections obtained from AAV NC and AAV shPMs mice. Scale bar, 40 um. (E) Quantification of the RNA levels of PM and Cbln1 obtained from B. Data are shown as means ± SEMs, n = 3. (F) Quantification of the protein levels of Cbln1 obtained from C. (G) Quantification of the GC numbers. (H) Evaluation of the control and shPMs-injected mice on cylinder test. Cylinder test was designed to assess limb preference on mice. It showed that compared with the control mice, PM shRNA-injected mice exhibited asymmetric high frequency in forepaw usage. The paw usage was counted and analyzed by normal-impaired/all. Data are shown as means ± SEMs, n = 7 (per group). (I) Evaluation of the control and shPMs-injected mice on rotarod test. Latency to fall provides the quantification of motor ability on the accelerating rotarod. It showed that compared with the control mice, shPMs-injected mice exhibited significant reduced duration in latency to fall. Data are shown as means ± SEMs, n = 6 (per group). (J) Representative electron microscope images for the control and shPM-injected mice. Red asterisk: intact synapse. Yellow triangle: free spine. Scale bar, 500 nm. (K) Quantification of the numbers of intact synapses obtained from J in the indicated treatments. (L) Quantification of the numbers of free spines obtained from (J) in the indicated treatments. All the data of this figure can be found in the S1 Data file. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Cbln1, Cerebellin-1; GCL, granule cell layer; lncRNA-PM, lncRNA-Promoting Methylation; ML, molecular layer; PCL, Purkinje cell layer; WM, white matter.
