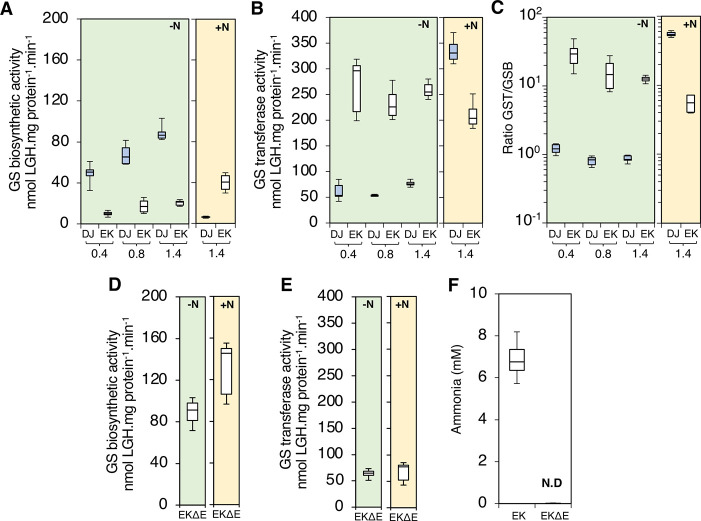
Fig 2. Ammonia excretion is dependent upon lower glutamine synthetase biosynthetic activity in the nifA-E356K strain (EK).
(A) Glutamine synthetase (GS) biosynthetic and (B) transferase activities were measured in the wild type (DJ, blue box plots) and E356K (EK, white box plots) strains in three different phases of growth, corresponding to an O.D600 nm of 0.4, 0.8 and 1.4 as indicated. Ratio between GS transferase (GST) and GS biosynthetic (GSB) activities is presented in (C) on a log10 scale to emphasize that the ratio between GST and GSB activities are close to 1 in the wild type (DJ) in all growth phases. (D) Glutamine synthetase (GS) biosynthetic and (E) transferase activities measured in the EKΔE strain (nifA-E356K with a glnE deletion) at an O.D600 nm of 0.8. The charts shaded in green represent the activities under diazotrophic conditions (-N), while those shaded in yellow represent the activity in the presence of excess fixed nitrogen, (20 mM NH4Cl, +N). (F) Ammonia from the culture supernatant was quantified in both the EK and EKΔE strains grown under diazotrophic conditions. N.D: not detected.