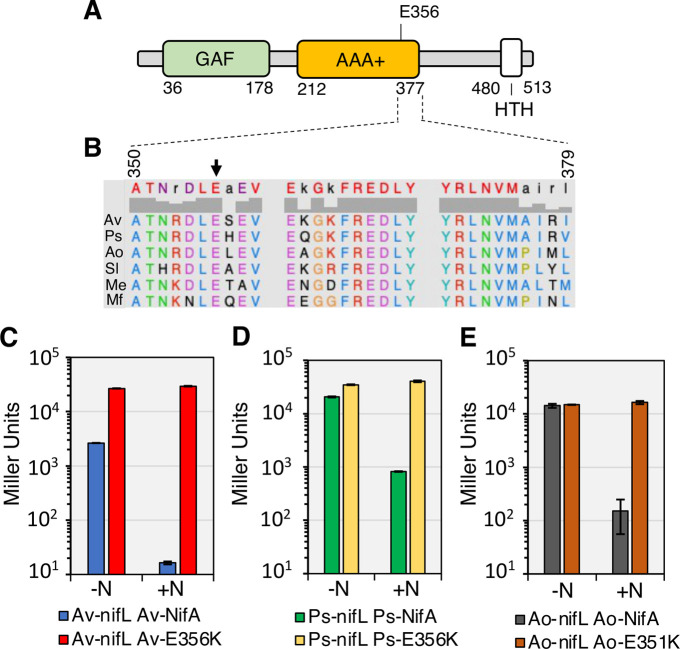
Fig 4. Reciprocal amino acid changes (related to nifAE356K in A. vinelandii) yield constitutively active NifA in Proteobacteria.
(A) Diagram of the A. vinelandii NifA domains. (B) Alignment of residues close to E356 (black arrow) in the central AAA+ domain of NifA proteins regulated by NifL. Sequence numbers refer to A. vinelandii NifA. Sequences used in the alignment are Av: A. vinelandii DJ, Ps: Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 (Gammaproteobacteria), Ao: Azoarcus olearius DQS4, Sl: Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1 (Betaproteobacteria), Me: Martelella endophytica YC6887 (Alphaproteobacteria) and Mf: Mariprofundus ferrooxydans M34 (Zetaproteobacteria). Panels C to E show β-galactosidase activities in the E. coli ET8000 chassis resulting from activation of a nifH::lacZ fusion (plasmid pRT22) by wild type and variant NifL-NifA systems from three different diazotrophs. Plasmids used to express NifL-NifA variants are as follows. (C) pPR34: Av-NifL-NifA, pPMA: Av-NifL-NifA-E356K; (D) pMB1804: Ps-NifL-NifA, pMB1805: Ps-NifL-NifA-E356K; (E) pMB1806: Ao-NifL-NifA, pMB1807: Ao-NifL-NifA-E351K. The assays were performed in NFDM media supplemented with 2% glucose in either nitrogen-limiting (200 μg/ml of casein hydrolysate, -N) or nitrogen excess (7.56 mM ammonium sulphate, +N) conditions.