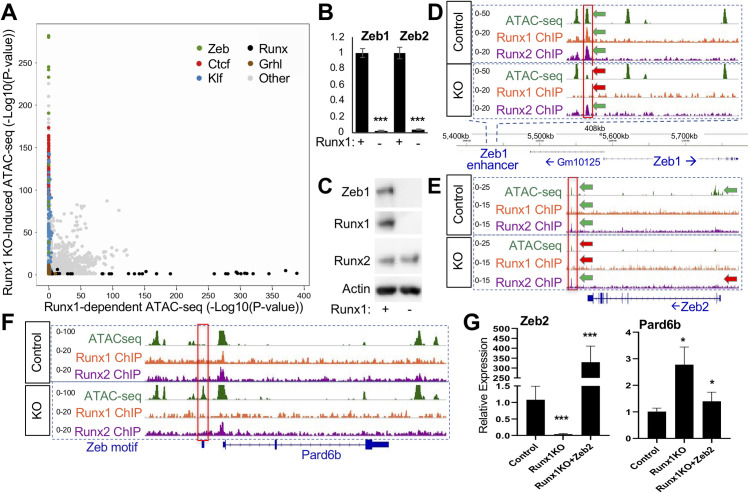
Fig 4. Runx1KO Cells Lack Zeb Repressors, Leading to the Opening of Chromatin.
A) Graph displaying p-values of transcription factor motif enrichment in Runx1-dependent versus Runx1-induced ATAC-seq, revealing that Zeb motifs are specifically enriched in Runx1KO-Induced ATAC-seq peaks. Additionally, Ctcf, Klf, and Grhl motifs are enriched in the Runx1KO-induced ATAC-seq peaks, while Runx motifs are enriched in the Runx1-dependent ATAC-seq. Note that this graph has had AP-1 motif enrichment results removed in order to focus on other motif enrichment levels (see S6A Fig for all transcription factor motifs). B) RT-qPCR showing that Runx1KO cells lose expression of Zeb1 and Zeb2. C) Western blot showing the absence of the Zeb1 protein in Runx1KO cells. D) Genomic snapshot showing a chromatin region near Zeb1 that is bound by Runx1 and Runx2 and loses chromatin accessibility in Runx1KO cells. E) Genomic snapshot of the Zeb2 locus showing a downstream potential enhancer bound by Runx1 and Runx2 that has decreased chromatin accessibility along with a loss of expression in Runx1KO cells. F) Genomic snapshot of the Zeb target gene Pard6b locus showing a promoter region containing a predicted Zeb binding site that is specifically open in Runx1KO cells. G) RT-qPCR showing that Zeb2 transient transfection of Runx1KO cells induces repression of Pard6b expression down to levels similar to those in control cells after 1 day of selection for transfected cells followed by 2 days of growth in media. (* = p-value < 0.05, ** = p < 0.005; *** = p-value < 0.0005).