Figure 2. Selection and evolution of proteins by mRNA display.
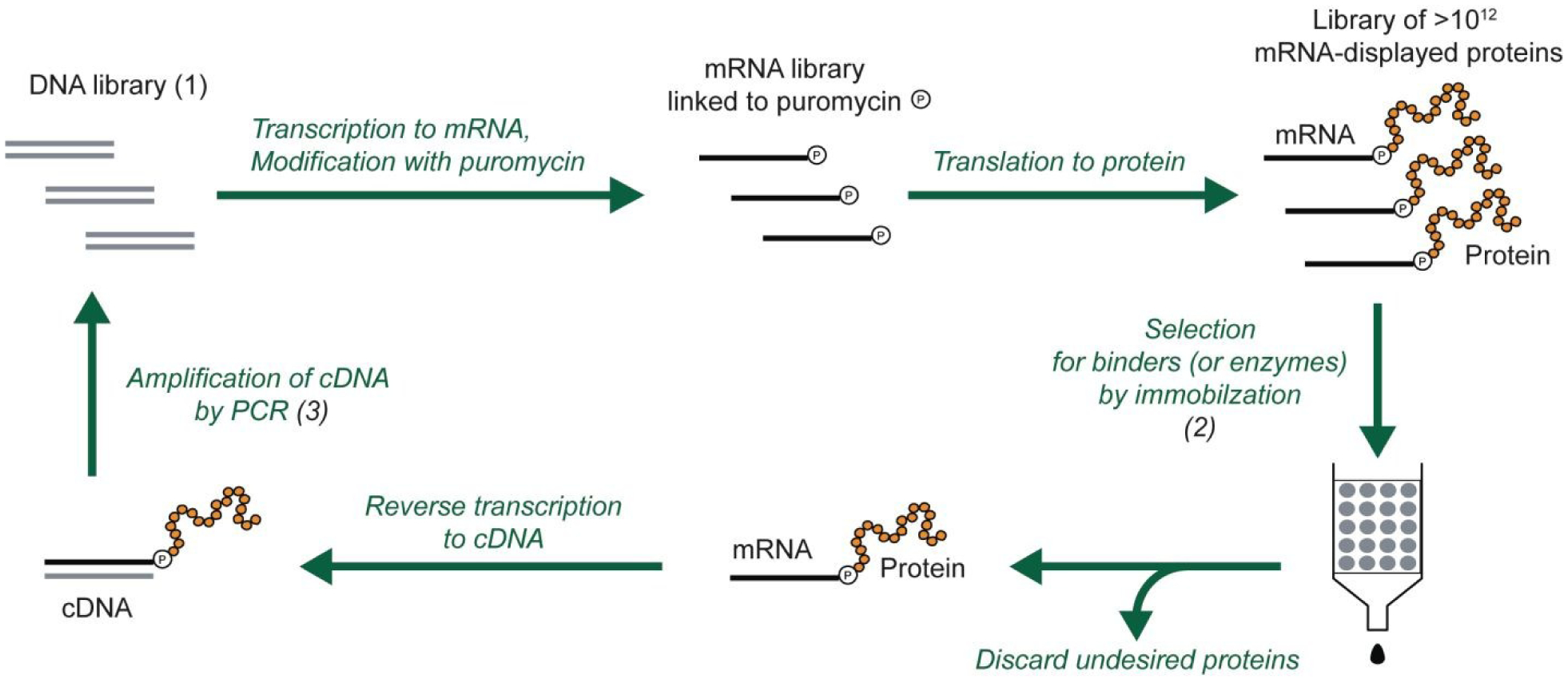
The procedure begins with a library of DNA (1) that encodes the library of protein variants. The DNA is transcribed into RNA, modified with puromycin and translated to mRNA-displayed proteins. In the selection step (2), the protein variants with the desired properties are separated from the undesired proteins. The selected variants are reverse transcribed to cDNA (can also be done before the selection step), and multiplied by PCR amplification (3). This round of selection and amplification is repeated until the resulting library is dominated by proteins with the desired properties. For protein evolution, the amplification step can be modified to introduce additional diversity (e.g., mutations).
