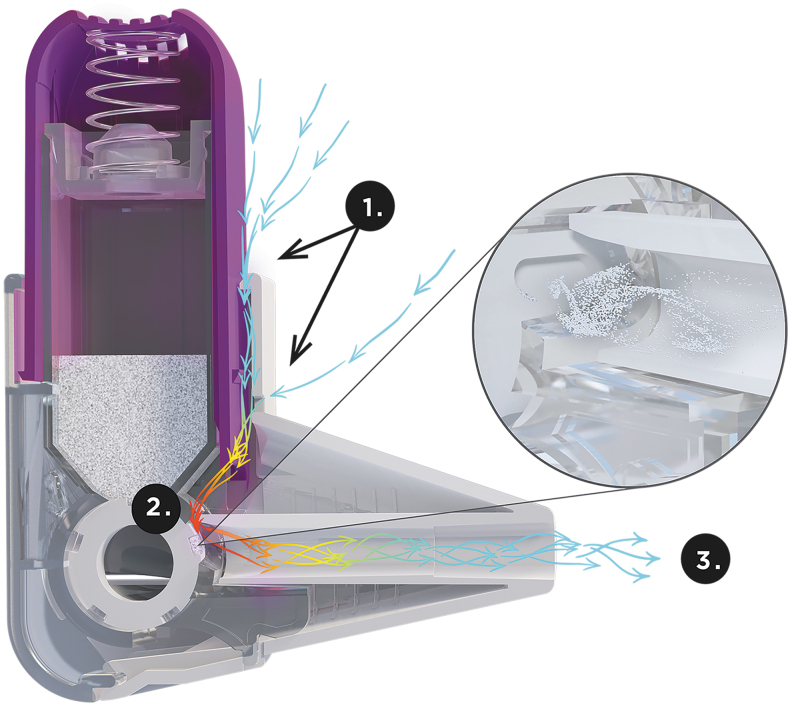
FIG. 1.
Cross-sectional diagram of the Easyhaler. When the patient inhales, air enters the Easyhaler around the actuator and encounters high or medium-to-high resistance due to the small size of the air vent (1); the resistance generates turbulent air flow to the dosing cup (2); turbulent air flow ensures deaggregation of drug particles and high dose emissions, even with low patient inhalation flows (3).