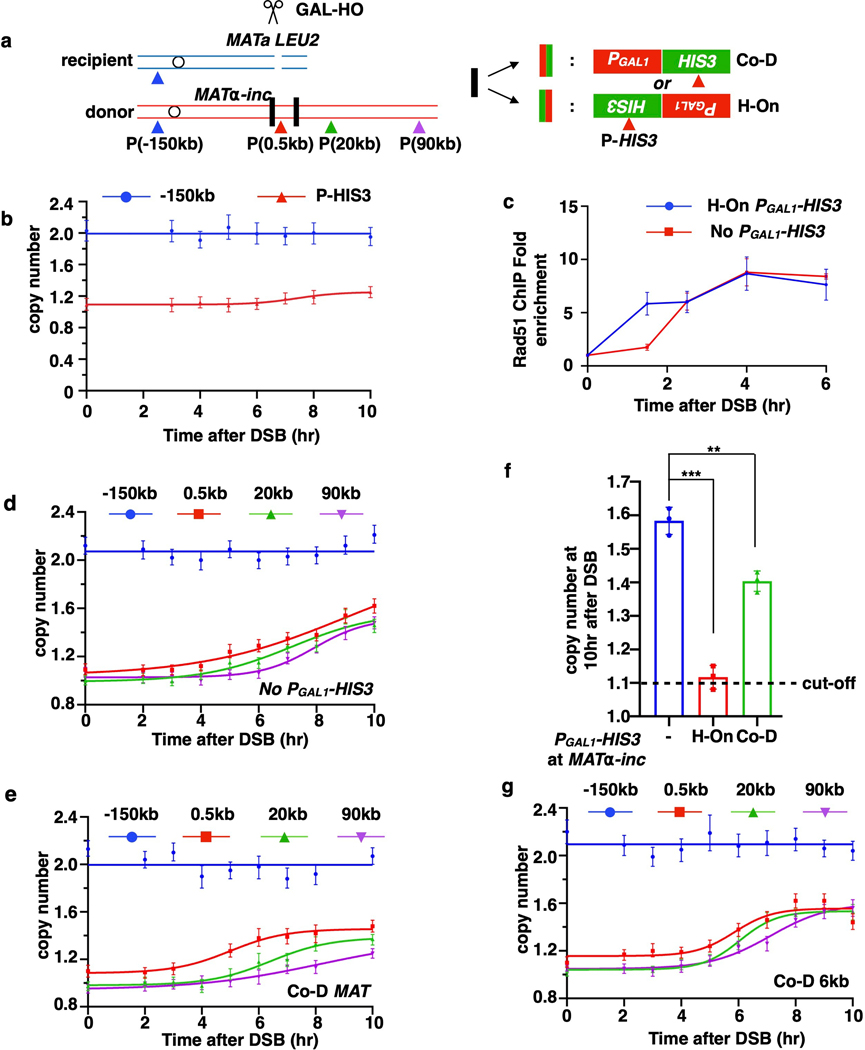
Extended Data Figure 8. Interference between BIR and transcription.
a, Schematic of PGAL1-HIS3 inserted at MATα-inc in H-On or Co-D orientations with respect to BIR progression. The same primer pairs were used for AMBER analysis as described in Fig. 1a, although their actual positions along the BIR track (donor chromosome) are shifted by insertion of PGAL1-HIS3. b, AMBER analysis of experiment in Fig. 4b using primers located in HIS3 gene. c, Strand invasion kinetics for experiment shown in d and Fig. 4b assessed by Rad51 ChIP followed by qPCR using primers amplifying the junction region with the forward primer targeting a donor and recipient shared region while the reverse primer targeting donor-specific region. The means ± SD (n=3 independent biological repeats) are indicated. d, AMBER analysis of AM1411 (the NO-PGAL1-HIS3 control strain used for experiments shown in Fig. 4b, and Extended Data Fig. 8e) containing insertion of lys2 under its native promoter at MATα-inc to match the experimental strains in mating type and in the presence of insertion at MATα-inc. e, AMBER analysis in strain with PGAL1-HIS3 inserted at MATα-inc in Co-D orientation. f, The amount of BIR synthesis detected at 10 hr using 0.5 kb primers in strains with or without PGAL1-HIS3. The means ± SD (n=3 independent biological repeats) are indicated. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference determined by two-tailed t-test (***: p=1.12e-4; **: p=0.0035) g, AMBER analysis of BIR progression in strains with PGAL1-HIS3 inserted 6 kb centromere distal from MAT in Co-D orientation. b, d, e, and g each represents one out of three independent biological repeats that showed similar results (see Supplementary Table 6 for other repeats). Mean values of target to reference (ACT1) loci ratios were calculated by Poisson distribution based on 10,000 droplets with error bars representing upper and lower Poisson 95% CI.