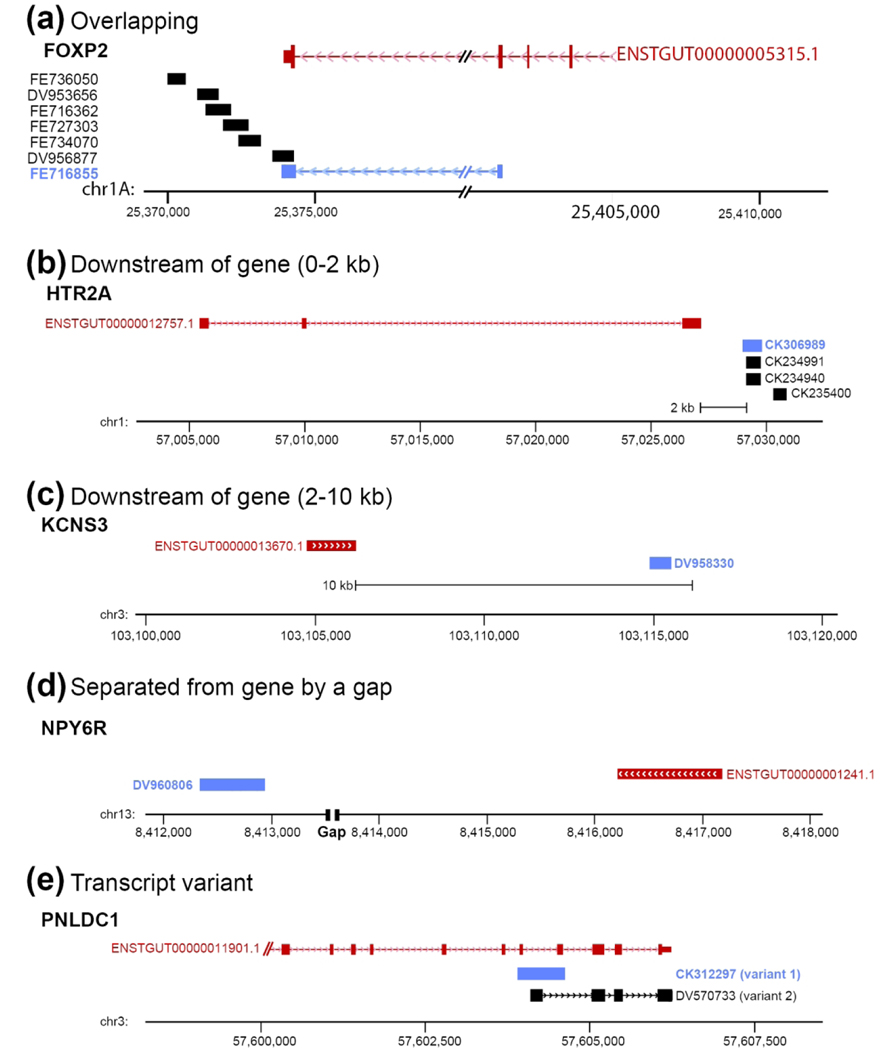
Figure 3. In Situ Probe Classification.
(a) Example of overlapping probe type: schematic depiction of genomic region for the zebra finch FOXP2 gene (based on UCSC’s genome browser) shows that clone FE716855 (Genbank ID shaded in red) was selected because it overlaps with coding and non-coding (3’-UTR) portions of the FOXP2 Ensembl Gene model (ENSTGUG00000005315.1). The EST for this clone also aligns unambiguously to this locus. Therefore, the Probe Location in the FOXP2 Gene Info page is listed as ‘Overlaps gene’. We note that the FOXP2 gene and related clones are on the minus strand (indicated by arrowheads in the gene model and selected clone alignments). (b-d) Examples of non-overlapping probes according to clone location relative to the gene. In (d), ‘Gap’ refers to a gap present in the genome assembly (taegut1). (e) Example of apparent spliced variants, where only one variant (CK312297) was analyzed. In all panels, Ensembl models are in red, clones selected for in situs are in blue, and orientation of gene and related clones are indicated by the arrowheads in the model and/or alternative variant clone. For each gene in ZEBrA the chromosomal location of the selected clone is listed under Probe Location in the Gene Info Page