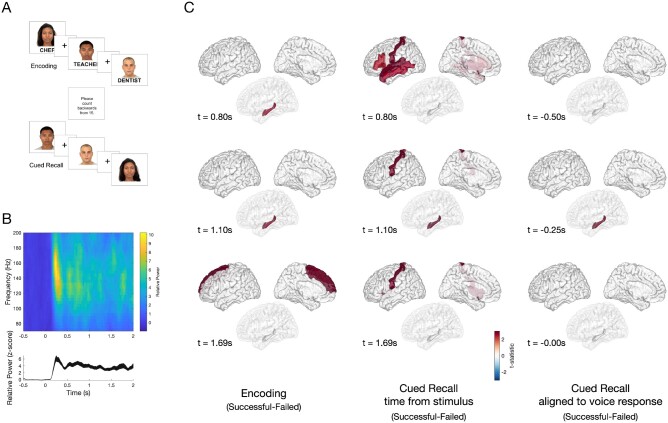
Figure 1.
Task design and differences in HGA between successful and failed associative memory. (A) A computerized program presented task stimuli and recorded subject spoken responses. During encoding, each face-profession pair was shown for 5 s, with a 1-s interstimulus interval (ISI), which was marked by a plus symbol. To ensure attention and sensory processing of test stimuli, subjects were instructed to read the profession aloud and make a mental association. To prevent rehearsal, a brief distraction task followed the encoding block, during which subjects were asked to count backwards from 15. During cued recall, subjects were shown only the faces from the prior set and asked to say aloud the associated profession. The cued recall period lasted for as long as the subject needed to provide a response. Voice response was recorded for the last 10 subjects and scored for accuracy. (B) Example spectrogram (top) of the raw data recorded in the occipital cortex, and high gamma activity (bottom, HGA 60–170 Hz) normalized to the −500 prestimulus baseline, with a peak at 250 ms after stimulus presentation. (C) Group-level differences in HGA by time for correctly versus incorrectly recalled face-profession pairs thresholded at P < 0.05 (cluster-corrected) during encoding (left), cued recall (middle) and vocal-aligned cued recall (right). Left: During encoding, increased HGA in hippocampus beginning approximately +0.80s after stimulus presentation, with increased HGA in superior frontal region beginning approximately +1.69 s distinguished between successful and failed trials. Middle: During cued recall, increased HGA at +0.80 s after face stimulus presentation in inferior frontal gyrus, postcentral, superior temporal and middle temporal gyrus, and later at +1.10 s in hippocampus distinguish between successful and failed trials P < 0.05, cluster-corrected). Right: To disambiguate the contribution of vocalization to cued recall, the difference between successful and failed trials was determined, timed in response to the vocalization in 10 patients. A difference in hippocampal HGA was seen beginning at −250 ms prior to vocalization (all significant clusters identified at a significance threshold P < 0.05 using a cluster-based permutation test).