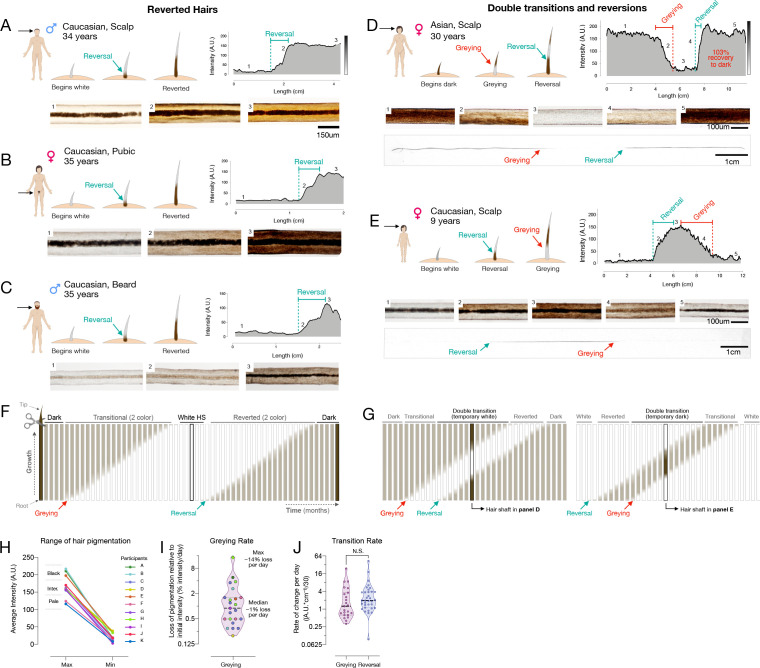
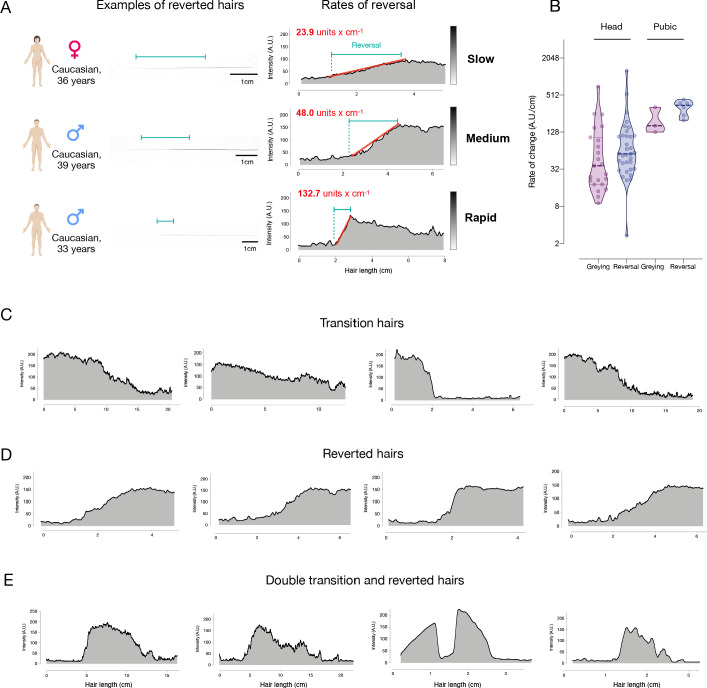
Figure 2. Reversal of hair greying across ages and body regions.
(A–G) Examples of HS greying and reversal including schematic of hair growth (top left), digitized HPP (top right), and light microscopy images (bottom) corresponding to numbered HS segments on the HPP plot. (A) Examples illustrating the reversal of greying along the length of scalp, (B) pubic, (C), and beard human HSs. (D) Example of segmental HS with double transitions, including temporary greying and (E) temporary reversal from an adult and a child, respectively. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for additional examples and Video 1 for animation. (F) Time course diagram illustrating the progression of a single dark HS undergoing greying followed by reversal back to its original color, and (G) closely occurring events of greying and reversal occurring, producing HS with double transitions. (H) Average maximum and minimum pigmentation intensity among transitioning hairs from participants with two-colored hairs (n = 11). Hairs with an average maximum intensity >180 A.U. are categorized as high intensity (black), 140–180 A.U. as intermediate intensity, and 100–140 A.U. as low intensity (pale color), indicating that these findings generalize across a range of pigmentation densities. (I) Rate of depigmentation per day in greying HS (n = 23), measured from the slope on HPP graphs expressed as % of starting intensity loss per day (assuming growth rate of 1 cm/month). (J) Comparison of the absolute rate of pigmentation change per day in greying (n = 23) and reverted (n = 34) HS. (I) and (J) are reported on a log2 scale to facilitate visualization.