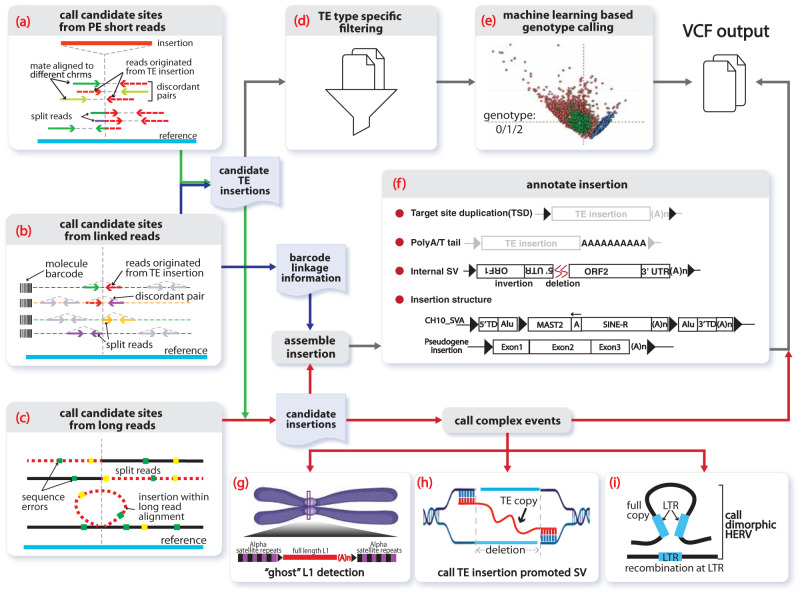
Fig. 1. Overview of TE analysis using xTea.
First, xTea identifies candidate insertion sites from three possible sets of data (or a hybrid): a paired-end Illumina short reads. b 10X Linked Reads, or c long reads. d Second, xTea filters candidate sites called from short reads for each specific transposable element (TE) type. e Third, for identified TE insertions, xTea uses a machine learning-based approach to call genotypes from short reads. f Fourth and finally, xTea annotates TE insertions and other retroelement insertions. g A schematic of a ‘ghost’ full-length L1 insertion detected from the centromere. h xTea can identify TE insertions that promote structural variation (SV) formation. i xTea can also identify dimorphic HERVs with given reference LTR locations.