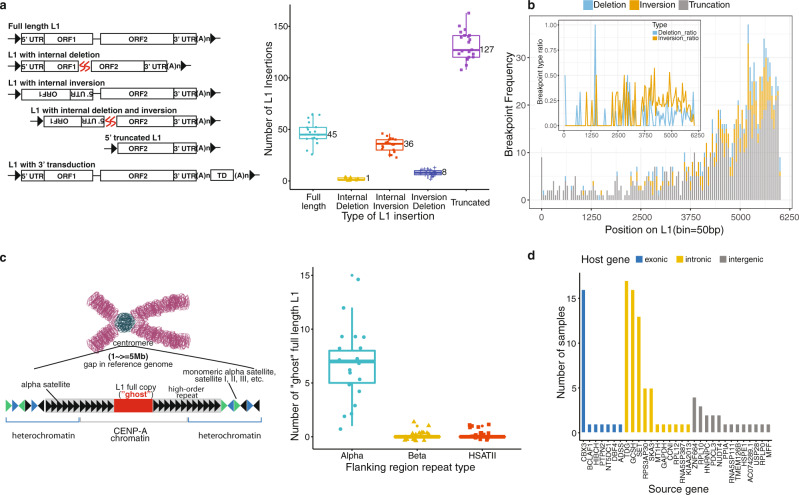
Fig. 4. L1 and processed pseudogene insertion from long reads.
a Left is the scheme of different types of L1 insertions, including the full-length L1, L1 with internal deletion, L1 with internal inversion, L1 with both internal deletion and inversion, 5’ truncated L1 and L1 with transduction. The boxplot at right shows the number of detected L1 insertions of those 5 types for the 20 long-read samples. b We checked the internal deletion, internal inversion, and truncation breakpoint frequency by position on L1 for all the detected non redundant L1 insertions. More internal deletions, internal inversions, and 5’ truncations happen at the tail side. The inset figure shows the normalized ratio for internal deletion and inversion by position, which indicates higher inversion rates than deletion from position ~4000 to the end. c Left is the scheme of centromere full-length L1. Right is the number of centromere ‘ghost’ full-length L1 copies per sample. On average per sample, we detected about 7, 1, and 1 full-length L1 copies flanked with Alpha, Beta, and HSATII satellite repeats, respectively. d 31 pseudogene insertions were detected from the 20 samples, including 7, 11, and 13 pseudogene insertions falling within exonic, intronic, and intergenic regions, respectively. 20 (64.52%) of the insertions are only detected in one sample. For the boxplots in a and c, the box demarcations represent the 25, 50, and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers extend from the box to the largest and smallest data points at most 1.5 times the interquartile range away from the median.