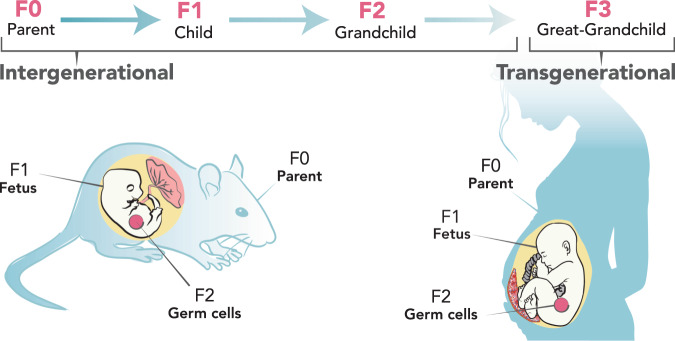
Fig. 1. Intergenerational and transgenerational inheritance.
Depiction of inheritance patterns from the parent (F0) generation to the child (F1), grandchild (F2), and great-grandchild (F3) in humans and animals. An exposure in F0 can directly affect the developing fetus (F1) and the germ cells in F2; therefore, both routes of transmission are considered intergenerational. Transgenerational effects may be observed beginning with the F3 generation.