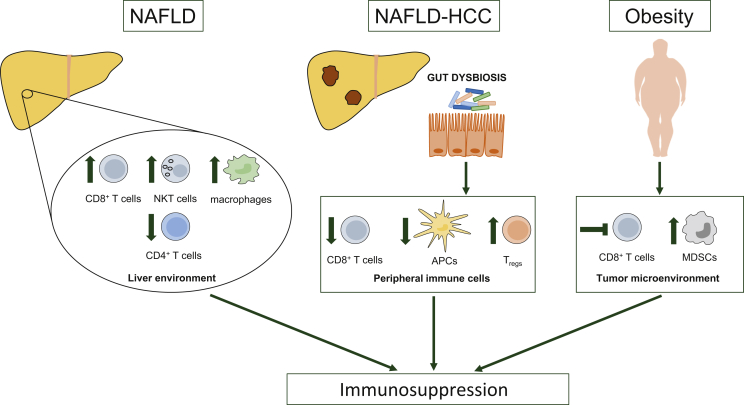
Figure 2.
Factors promoting immunosuppression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
NAFLD impacts the liver immune microenvironment. While the number of CD4+ T cells with antitumor functions is reduced, CD8+ T cells, NKT cells, and macrophages with tumor-promoting properties expand in NAFLD. Gut dysbiosis in NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma promotes peripheral immunosuppression, characterized by reduced numbers of CD8+ T cells and antigen-presenting cells and expansion of regulatory T cells. Obesity is a risk factor for NAFLD and thus frequently present in patients with NAFLD. Obesity impairs the function of CD8+ T cells and enhances the immunosuppressive potency of tumor-infiltrating MDSCs.
APCs, antigen-presenting cells; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NKT cells, natural killer T cells; Tregs, regulatory T cells.