FIGURE 2.
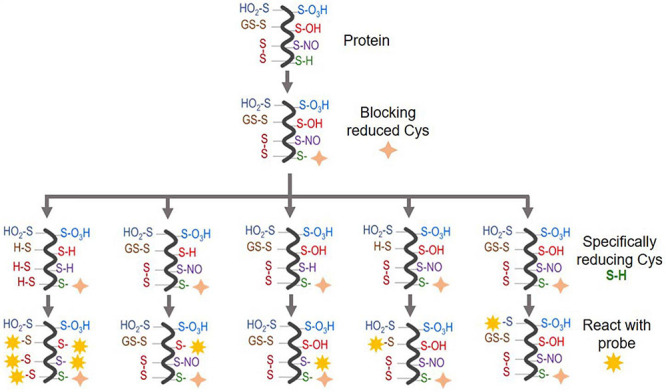
An overview of Oxi-Cys quantitative proteomics approaches for different types of Cys oxidations. Chemicals used for selective Oxi-Cys proteomics analysis. Free reduced Cys residues are firstly labeled with alkylating reagents (IAM, NEM, MMTS, etc.) while different PTMs of reversible Oxi-Cys residues are selectively alkylated by specific reducing regents; for example, DTT/TCEP for reducing all reversible Cys, arsenite for S-sulfenylation (S-OH), ascorbate for S-nitrosylation (S-NO), glutaredoxin for S-glutathionylation (S-SG). These newly formed reduced Cys residues then, theoretically, can be labeled by different alkylating reagents or specific probes coupled with tags for purification/enrichment. The quantitation is performed based on comparing intensities of tags from diseased compared to control groups. S-OH probes include: dimedone and bicyclononyne BCN; S-O2H probes include: C-nitroso esters, diazenes and S-nitrosothiols as detailed in Figures 5A,B.
