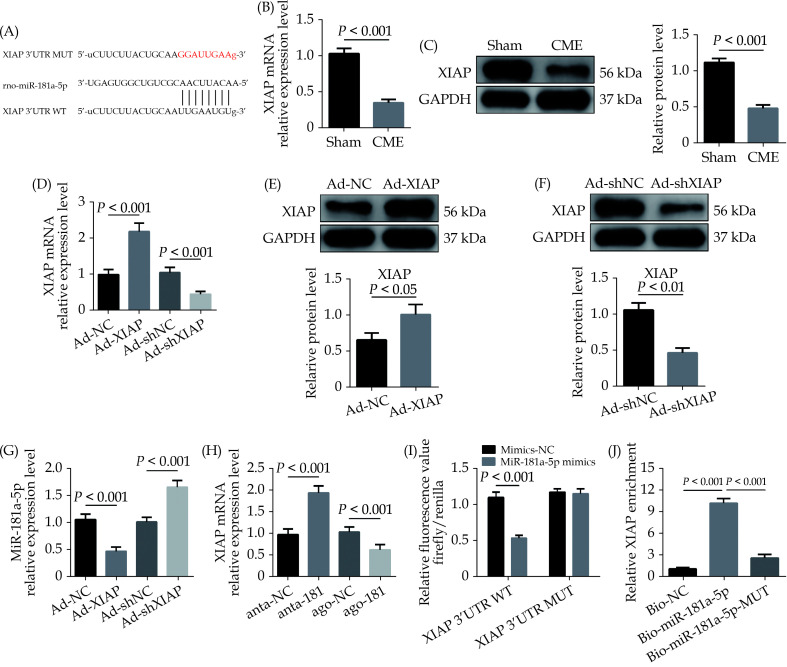
Figure 4.
XIAP is a direct target of miR-181a-5p.
(A): The predicted binding region between miR-181a-5p and XIAP mRNA was predicted by using bioinformatics analysis; (B): XIAP mRNA level was significantly decreased after CME (n = 10); (C): XIAP protein level was significantly decreased after CME (n = 3); (D): XIAP mRNA was overexpressed or silenced with Ad-XIAP or Ad-shXIAP, the qRT-PCR was used to detect the transfection efficiency (n = 10); (E): transfection with Ad-XIAP increased myocardial XIAP protein level significantly (n = 3); (F): transfection with Ad-shXIAP decreased myocardial XIAP protein level significantly (n = 3); (G): the expression level of miR-181a-5p was tested in XIAP-upregulated or XIAP-overexpressed rats with qRT-PCR (n = 10); (H): the expression levels of XIAP were tested in miR-181a-5p-downregulated or miR-181a-5p-overexpressed rats with qRT-PCR (n = 10); (I): relative luciferase activity in WT-XIAP and MUT-XIAP; and (J): RNA pulldown assay was applied to prove the binding relation between XIAP and miR-181a-5p. Data were shown as mean ± SE (standard error) based on at least three independent experiments. CME: coronary microembolization; MUT: mutant; qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; WT: wild-type; XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.