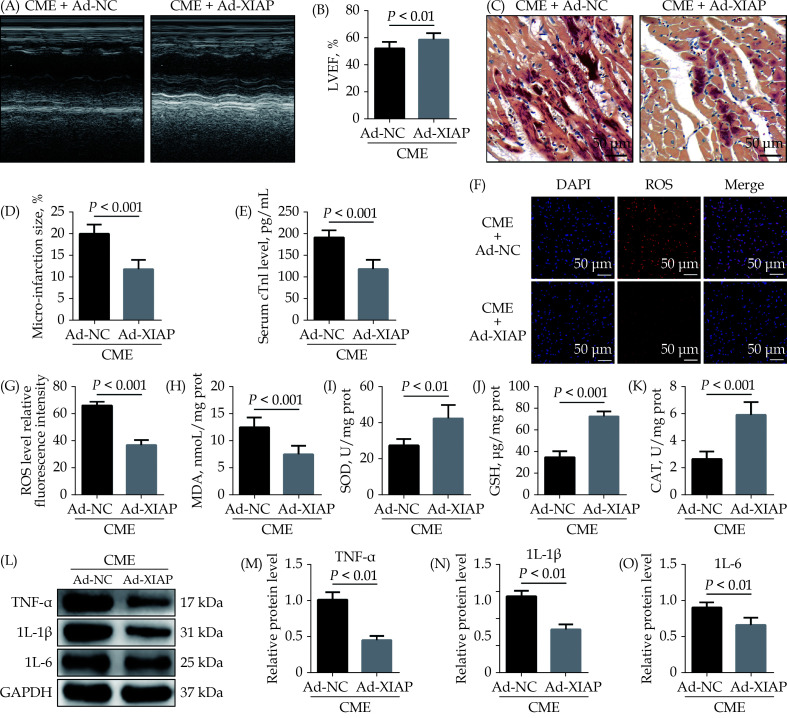
Figure 5.
Overexpression of XIAP ameliorates CME-caused myocardial oxidative stress and inflammatory injury.
(A & B): Echocardiography was used to assess cardiac function and to quantify LVEF ( n = 10); (C & D): haematoxylin-basic fuchsin-picric acid staining was used to measure micro-infarction size (× 200 magnification, scale bar = 50 µm) ( n = 6); (E): serum cTnI concentration in each group (n = 10); (F & G): the ROS production was detected by the dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate assay (× 200 magnification, scale bar = 50 µm) ( n = 6); (H–K): myocardial MDA, SOD, GSH, and CAT level in each group (n = 6); and (L–O): western blotting was used to quantify myocardial TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 protein level, with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a loading control (n = 3). Data were shown as mean ± SE (standard error) based on at least three independent experiments. CAT: catalase enzymes; CME: coronary microembolization; cTnI: cardiac troponin I; GSH: glutathione; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin 6; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MDA: malondialdehyde; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.