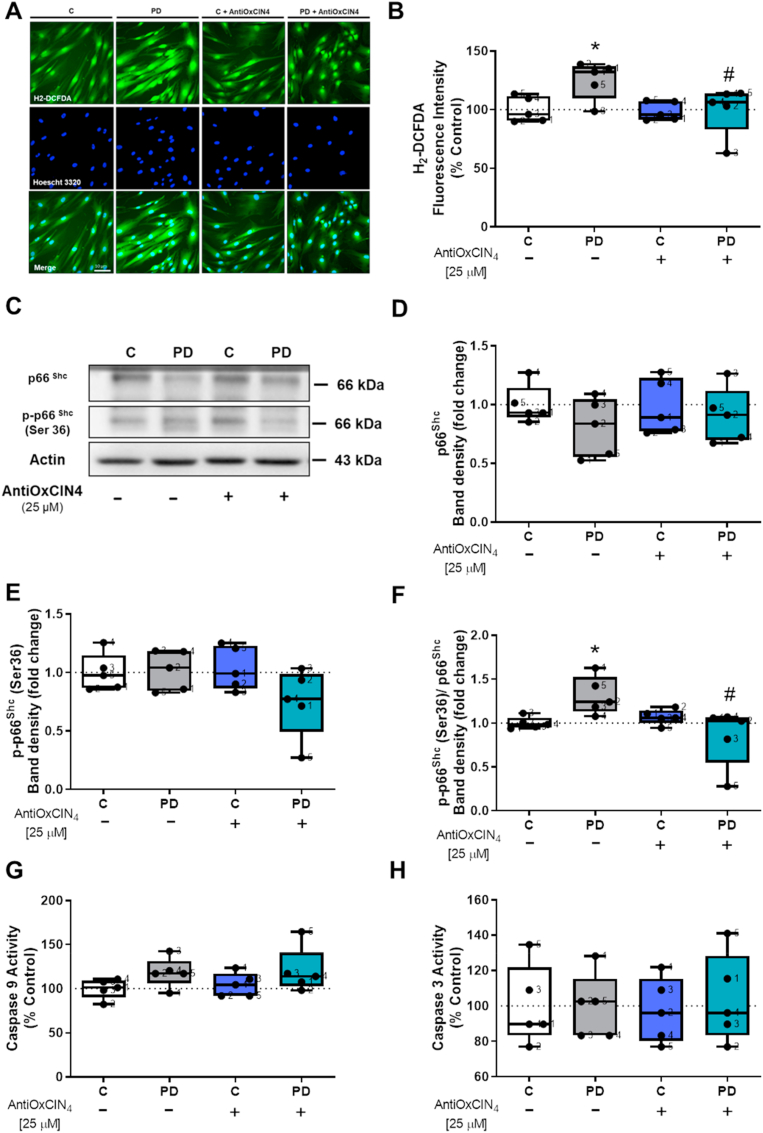
Fig. 11.
AntiOxCIN4treatment of fibroblasts from sPD patients decreased H2-DCFDA oxidation. H2-DCFDA intensity fluorescence of human skin fibroblasts from sPD and their matched-controls were measured by epifluorescence microscopy (A). The quantification of H2-DCFDA fluorescence was obtained by ImageJ 1.45S program. Graphic is expressed as mean ± SEM of H2-DCFDA intensity fluorescence divided by area (B). Western blotting was used to detect total p66Shc (C and D), phosphorylation of p66Shc (p-p66Shc Ser36) (C and E) and the ratio between p-p66Shc Ser36 and total p66Shc (F) in total fractions from human skin fibroblasts cell lines. Actin was used as a loading control. Blots are representative of different cell preparations with a random distribution between C and PD. Caspase-9- (G) and caspase-3-like activities (H) were measured by the cleavage of the colorimetric substrates Ac-LEHD-pNA and Ac-DEVD-pNA, respectively. Caspase-like activity was expressed as the concentration of pNA released per μg protein. Known concentrations of p-NA were used as standards. Each measurement corresponds to one different individual (5 fibroblasts from sPD patients and 5 fibroblasts from respective sex- and age-matched healthy controls). Data was normalized on the control condition (C = 100% or C = 1.0 fold-change). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. Statistical significance was accepted with (*) p < 0.05 to C vs PD or C + AntiOxCIN4 vs PD + AntiOxCIN4 and (#) p < 0.05 to C vs C + AntiOxCIN4 or PD vs PD + AntiOxCIN4.