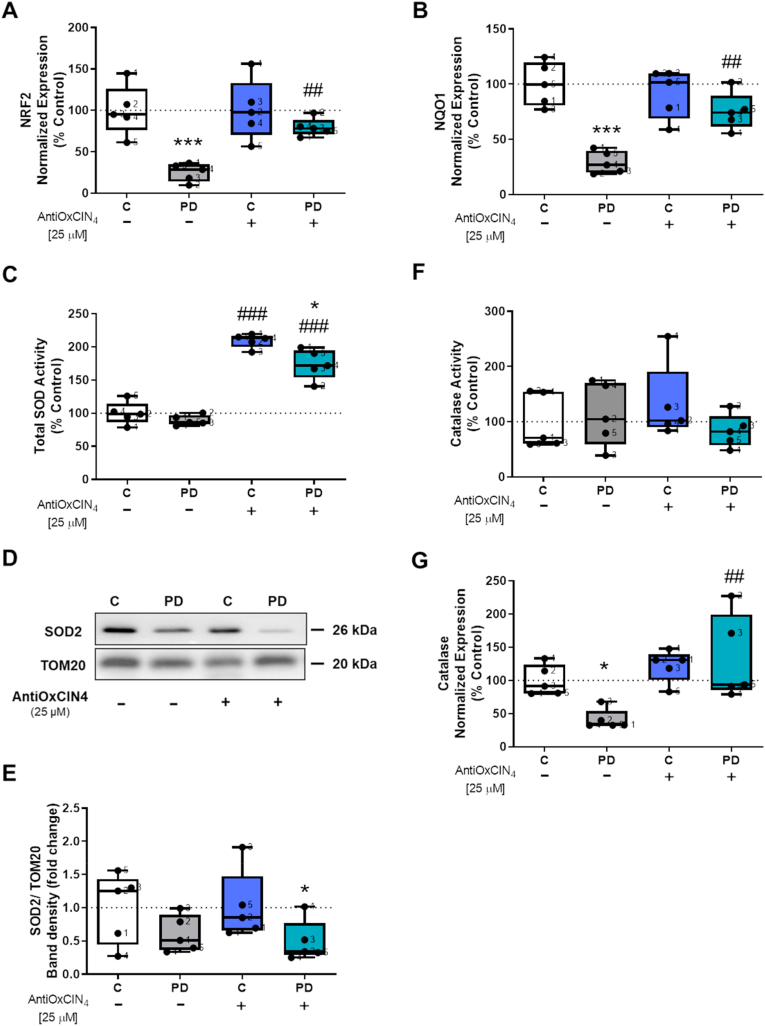
Fig. 9.
AntiOxCIN4treatment of fibroblasts from sPD patients increased total SOD activity and upregulated NRF2 and NQO1 gene expressions. Total RNA was extracted, converted into cDNA, and amplified by real-time RT-PCR. mRNA levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) (A), NADPH quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1) (B) and catalase (G) were measured. mRNA level was normalized to geometric mean of 4 housekeeping genes, including mitochondrial 37S ribosomal protein (MRPL51), hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1), C19orf74, family with sequence similarity 57 member A (FAM57A). Total superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (C) was measured using a commercially available kit, following the manufacturer's instructions. Western blotting was used to semi-quantify superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in total fractions from human skin fibroblasts cell lines (D and E). TOM20 was used as a loading control. Blots are representative of different cell preparations with a random distribution between C and PD. Catalase activity was determined by following hydrogen peroxide decomposition by measuring the 240 nm absorbance decrease (F). Each measurement corresponds to one different individual (5 fibroblasts from sPD patients and 5 fibroblasts from respective sex- and age-matched healthy controls). Data was normalized by the control condition (C = 100% or C = 1.0 fold-change). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 5 different experiments. Statistically significance was accepted with (**) p < 0.05, (***) p < 0.005 to C vs PD or C + AntiOxCIN4 vs PD + AntiOxCIN4 and (##) p < 0.01, (###) p < 0.005 to C vs C + AntiOxCIN4 or PD vs PD + AntiOxCIN4.