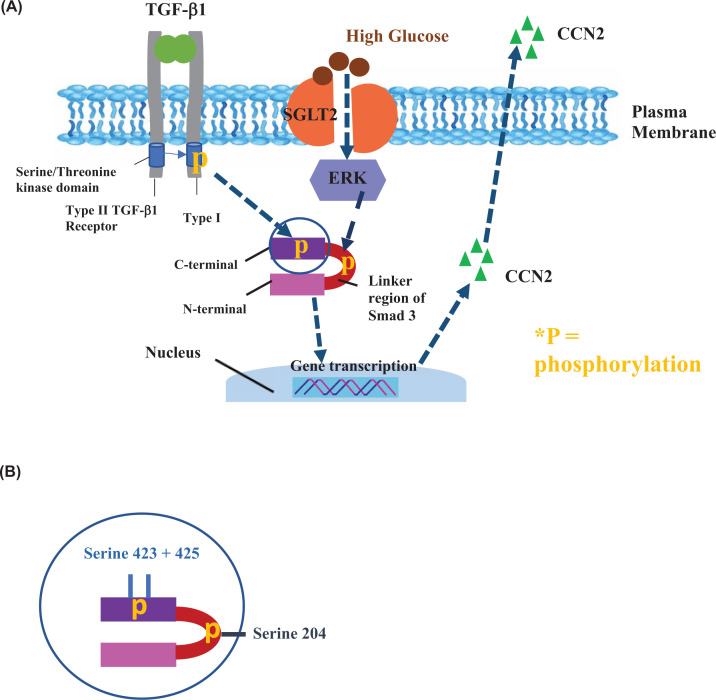
Figure 5. Schematic of proposed signalling mechanism: glucose mediated pro-fibrotic CCN2 induction.
(A) Typically, the TGF-β1 type 2 receptor phosphorylates the cytoplasmic domain of the type 1 receptor, which then proceeds to phosphorylate Smad3 on the MH2 domain, (B) specifically at serine 423 and 425. The fully activated Smad complex is then translocated to the nucleus where it controls gene transcription. Under hyperglycaemic conditions, ERK is also activated and phosphorylates the serine 204 located on the linker region between the C (SSXS) and N terminal domain. This then increases TGF-β specific signalling of the complex, thereby potentiating transcriptional activity at the nucleus. Control = 7 mM D-glucose, Control + TGF-β1 = 7 mM D-glucose + 0.75 ng/ml TGF-β1, D-Glu = 7 mM D-glucose + 18 mM D-glucose, L-Glu = 7 mM D-glucose + 18 mM L-glucose, D-Glu + TGF-β1 = 7 mM D-glucose + 18 mM D-glucose + 0.75 ng/ml TGF-β1, L-Glu + TGF-β1 = 7 mM D-glucose + 18 mM L-glucose + 0.75 ng/ml TGF-β1. This legend key is applicable to all subsequent figures.