Figure 3.
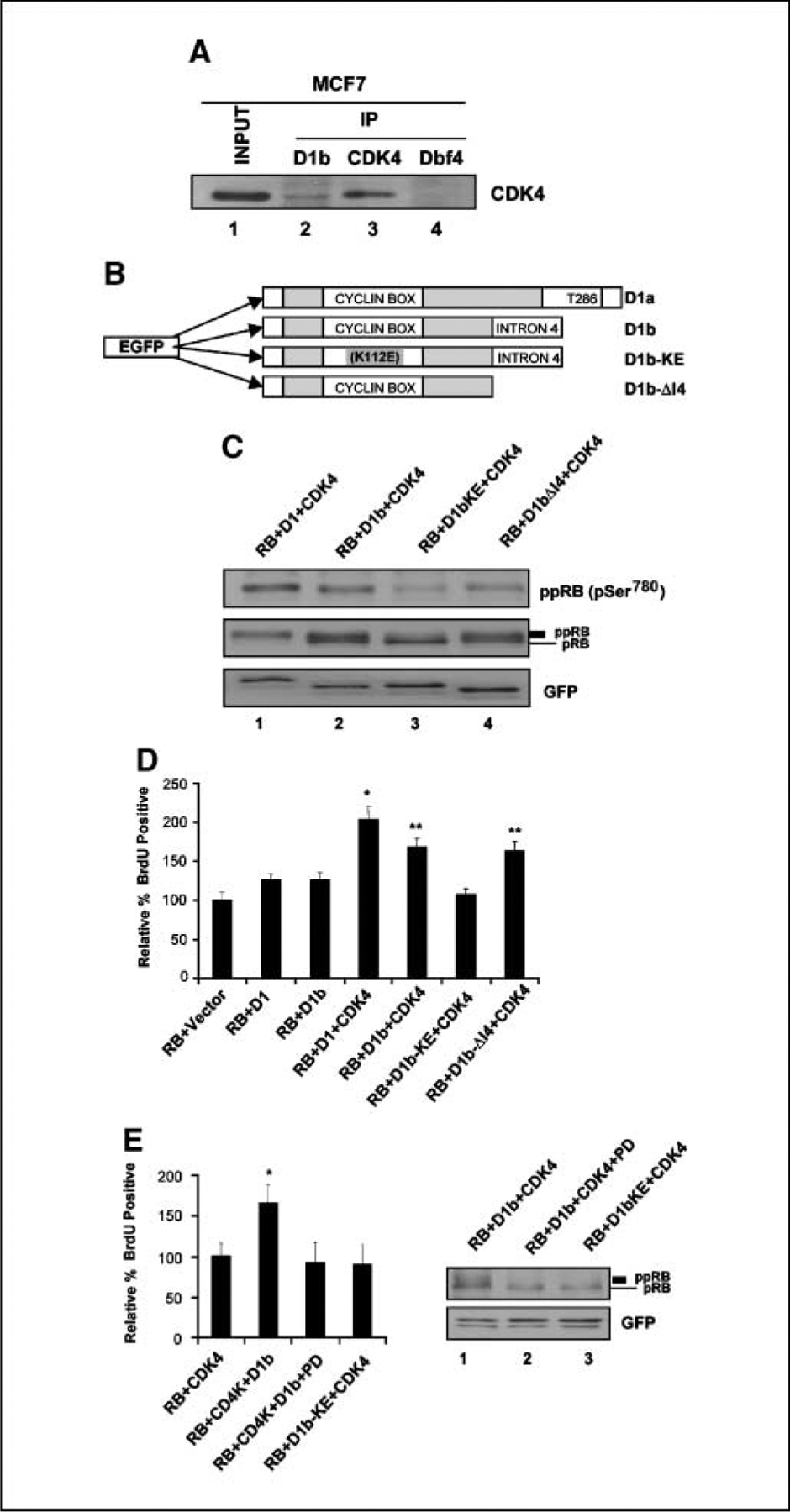
The functions of cyclin D1b strongly associate with CDK4 and its intron 4 regions. A, MCF-7 cells were harvested, and cell lysate was prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with specific cyclin D1b, CDK4, and Dbf4 antibodies. Input lysate and the resultant precipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE. CDK4 proteins were detected by immunoblotting. B, diagram depicting the mutant structures of cyclin D1b gene. The cyclin D1b–KE is a mutation of K112E. The mutant D1b-ΔI4 is encoded by the first four exons of cyclin D1 gene and the COOH terminal intron 4 has been deleted. Both D1b mutants are NH2 terminal GFP tagged proteins. C, SAOS-2 cells were cotransfected with the indicated expression plasmids. Total cellular protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE. RB, hyperphosphorylated RB, GFP-D1, D1b, and D1b mutant proteins were detected by immunoblotting. D, SAOS-2 cells were cotransfected with RB, CDK4, and the GFP-D1b, GFP-D1, and GFP-D1b mutants for 40 h and labeled with BrdUrd for 6 h. Cells were fixed and immunostained for relative BrdUrd incorporation to monitor S phase progression. Data shown are from two independent experiments with at least 200 cells counted for each experiment. *, P < 0.01 compared with RB + Vector; **, P < 0.05 compared with RB + D1 + CDK4. E, SAOS-2 cells were cotransfected and treated with vehicle (DMSO) or PD-0332991 as indicated. At 40 h posttransfections, cells were labeled with BrdUrd for 6 h. Cells were fixed and relative BrdUrd incorporation was determined from two independent experiments; *, P < 0.05 compared with RB + CDK4 (left). Lysates were prepared and RB detected by immunoblotting (right).
