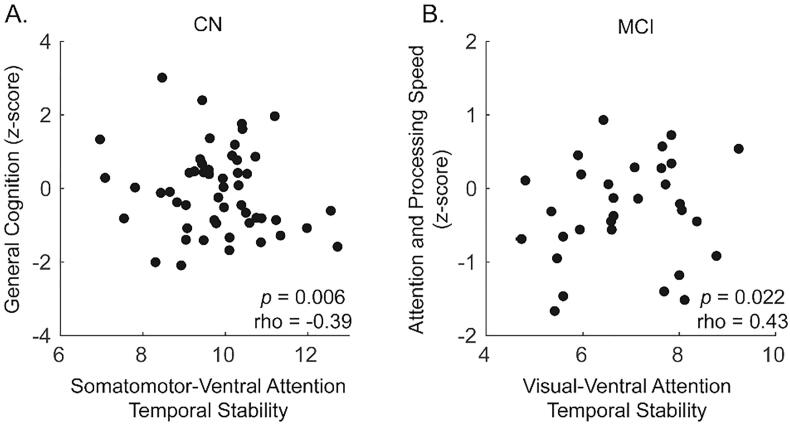
Fig. 7.
Significant within diagnostic group relationships (across both samples) between cognitive scores and temporal stability. (A) In the cognitively normal (CN) group, general cognition was negatively correlated with temporal stability of the Somatomotor and Ventral attention network interaction block. (B) In the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) group, attention and processing speed positively correlated with temporal stability of the Visual and Ventral Attention network interaction block. Data are shown for the 200 node parcellation data; 300 node parcellation data are shown in Supplementary Figure 10. Significance was determined as p < 0.05 (uncorrected) partial Spearman’s correlation (age, sex, and education adjusted) in 200 node data that was reproduced at pFDR < 0.05 in the 300 node data.